How to interpret hand X-rays: 3 Essential Methods
Introduction
Interpreting hand X-rays is a vital skill in orthopedics and other medical fields, offering crucial insights for diagnosing and treating patients. This guide introduces readers to hand X-rays and outlines three essential methods to interpret them.
Hand injuries are common and can occur in various settings, such as at home, work, or during sports activities. They can range from minor cuts and bruises to more serious conditions like fractures, dislocations, or tendon injuries. Hand X-rays are a primary tool for assessing the extent of these injuries, understanding the alignment of bones, and planning for surgical or non-surgical treatment. They are also crucial for monitoring the healing process and ensuring a successful recovery.
Understanding Hand X-rays
Hand X-rays are common imaging tests that capture images of the bones, joints, and soft tissues in the hand. This section will help you understand what hand X-rays are and when you might need one.
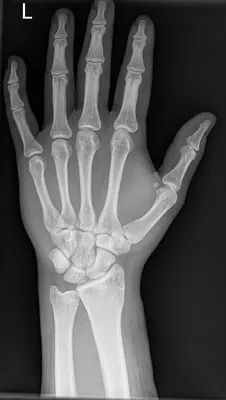
What Do Hand X-rays Show?
- Bone Conditions: Identification or monitoring of conditions such as fractures, arthritis, and bone tumors.
- Joint Conditions: Assessing the status of joints, including dislocations and arthritis.
- Foreign Objects: Locating foreign objects like metal fragments or splinters.
- Soft Tissue Swelling: Detecting swelling in the surrounding soft tissues.
When Will You Get One?
- Symptom Investigation: Persistent pain, swelling, deformity, or loss of function in the hand.
- Routine Check-ups: Especially for individuals with chronic joint conditions.
- Pre-surgical Assessment: Before certain surgeries to evaluate the structure and condition of the hand.
- Occupational Health Screenings: Monitoring bone health in individuals exposed to repetitive stress or vibrations.
Methods to Interpret Hand X-rays
Interpreting hand X-rays is a nuanced process that can be approached in various ways depending on your expertise, needs, and resources. Below, we delve into three distinct methods catering to different skill levels and circumstances.
1. Utilizing X-ray Interpreter
X-ray Interpreter is a robust online platform designed to provide quick and accurate interpretations of hand X-rays through AI technology. Follow these steps to easily obtain an AI-generated analysis of your X-ray images:
- Registration: Sign up on X-ray Interpreter to access the AI-based analysis.
- Uploading X-rays: Upload your hand X-ray images onto the platform.
- Reviewing Interpretation: Review the AI-generated interpretation and download the report.
- Seeking Professional Advice: If necessary, consult with medical professionals to understand the interpretation in a clinical context.
Please check out our get started guide.
2. Using ChatGPT Plus
ChatGPT Plus employs the powerful GPT-4V model to provide insightful analysis of hand X-ray images. This method offers a more interactive experience, allowing you to communicate with the AI and refine the analysis to suit your needs:
- Subscription: Subscribe to ChatGPT Plus to access GPT-4V for image analysis.
- Uploading X-rays: Navigate to the GPT-4V interface on the OpenAI platform and upload your hand X-ray images.
- Requesting Analysis: Request an analysis of the X-ray images by inputting natural language commands or questions.
- Reviewing and Confirming Analysis: Review the analysis provided, iterate to get more detailed or specific information if necessary.
- Consulting Professionals: Seek advice from medical professionals to validate the analysis provided by GPT-4V.
Please read our post on how to use ChatGPT Plus for X-ray analysis to learn more.
Alternatively, as several other AI models with vision capabilities emerge, you can also try other models, such as Grok by xAI, Claude by Anthropic, Gemini by Google Deepmind.
3. Reading X-rays by Yourself
Self-reading is a traditional method that relies on individual expertise and resources. It's ideal for medical professionals looking to hone their interpretative skills. This method requires a solid foundation in orthopedic knowledge and a willingness to continuously learn and improve:
- Education: Acquire basic knowledge and training on reading and interpreting hand X-rays from reputable sources or through coursework.
- Practice: Practice interpreting hand X-rays under the guidance of experienced professionals.
- Resources: Utilize books, online resources, and medical literature to enhance your understanding and skills in interpreting hand X-rays.
- Seeking Feedback: Obtain feedback from knowledgeable professionals to improve your interpretation skills.
- Continuous Learning: Continuously update your knowledge and skills by reading recent medical literature, attending workshops, and engaging in discussions with professionals.
Recommended Resources for Self-Reading:
-
X-ray Interpretation: Hand Injuries: This course on Radiopaedia provides a comprehensive overview of hand injuries, their radiographic investigations, and interpretations, complete with video commentary and review quizzes to test your understanding.
-
Hand X-ray Anatomy Quiz: This quiz on PurposeGames offers a fun way to test and enhance your hand X-ray interpretation skills with 34 questions covering various aspects of hand anatomy.
-
Trauma X-ray Quiz - Upper limb: Offered by Radiology Masterclass, this quiz provides a structured assessment after studying the course material available in their tutorials and galleries sections, making it a great resource for more formalized learning.
These resources offer a variety of learning materials and platforms to enhance your understanding and practice in hand X-ray analysis. Whether you prefer interactive quizzes, structured courses, or detailed tutorials, the above-mentioned resources cater to different learning preferences and levels of expertise.
Comparative Analysis
Choosing the right method to interpret hand X-rays is crucial for accurate and timely analysis, which can significantly impact patient care. Here, we present a comparative analysis of the three methods discussed in this guide: X-ray Interpreter, ChatGPT Plus, and Self-Reading. We evaluate these methods based on several criteria including accuracy, ease of use, cost, time efficiency, learning curve, and the provision of additional resources. This comparison aims to provide a clear understanding of what each method offers and help you make an informed decision based on your individual needs and circumstances.
| Criteria | X-ray Interpreter | ChatGPT Plus | Self-Reading |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Mostly High (AI-based)1 | Mostly High (AI-based)1 | Varies (Skill-dependent) |
| Ease of Use | Easy | Moderate | Challenging |
| Cost | Starting from $2.50 per image | $20 per month | Free (excluding educational costs) |
| Time Efficiency | Fast | Moderate to Fast | Slow to Moderate |
| Learning Curve | Low | Low to Moderate | High |
| Additional Resources | Provided | Partially Provided (through OpenAI) | Self-sourced |
The table provides a quick overview of how each method stacks up against the others across various criteria. It's essential to consider your level of expertise, the urgency of the situation, and the resources at your disposal when choosing a method for interpreting hand X-rays. For instance, if you require immediate interpretation with a high level of accuracy, leveraging AI-based methods like X-ray Interpreter or ChatGPT Plus may be more suitable. On the other hand, if you have a medical background and are looking to enhance your skills further, opting for self-reading and consulting additional resources might be the way to go. Each method has its unique advantages and challenges, and understanding these can help in selecting the most appropriate method for your needs.
Conclusion
Interpreting hand X-rays is a critical skill in the medical and orthopedic fields, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various musculoskeletal conditions. This guide provided an overview of three different methods to interpret hand X-rays: utilizing X-ray Interpreter, using ChatGPT Plus, and self-reading. Each method caters to different levels of expertise and circumstances, offering a range of options for individuals and professionals alike.
X-ray Interpreter and ChatGPT Plus harness the power of artificial intelligence to provide quick and accurate interpretations, making them suitable choices for those in need of immediate insights, regardless of their medical background. On the other hand, self-reading is a more traditional approach, ideal for medical professionals looking to hone their interpretative skills.
The comparative analysis presented in this guide aims to aid in making an informed decision based on individual needs, technical proficiency, and the resources at disposal. While AI-based methods offer a high level of accuracy and ease of use, self-reading provides an opportunity for continuous learning and professional development.
Furthermore, the guide highlighted several resources to aid in self-education for those interested in the self-reading method. These resources offer a wealth of information and practice materials to improve one's skills in hand X-ray interpretation.
In a rapidly evolving medical landscape, staying updated with the latest technologies and methodologies is crucial for providing accurate and timely patient care. Regardless of the method chosen, adhering to legal guidelines and ethical practices is paramount to ensure the privacy, safety, and wellbeing of individuals.
This guide serves as a starting point in exploring the various methods of hand X-ray interpretation, with the hope of aiding individuals and professionals in navigating this crucial aspect of medical diagnostics. The choice between these methods ultimately depends on personal preferences, professional goals, and the specific circumstances at hand.
Related Articles
Resources and Further Learning
For those interested in delving deeper into the realm of hand X-ray interpretation, a wealth of resources is available online. Whether you are a seasoned professional looking to refresh your knowledge or a student eager to learn, these resources offer invaluable insights and structured approaches to interpreting hand X-rays:
-
Hand radiograph (an approach) | Radiology Reference Article:
- A systematic checklist for reviewing musculoskeletal exams including soft tissue areas, cortical margins, trabecular patterns, bony alignment, and joint congruency.
-
Musculoskeletal (MSK) X-ray Interpretation – OSCE Guide:
- Provides a brief overview of MSK X-ray interpretation, including a structured approach you can apply to most X-rays and examples of relevant pathology.
-
Approach to Hand X-Rays · RheumTutor:
- Discusses a systematic ABCDs approach to interpreting hand radiographs, mainly for assessing fractures.
These resources cater to different levels of expertise and provide varied approaches to hand X-ray interpretation, aiding in the enhancement of your skills and understanding in this critical aspect of medical diagnostics.