Stay Ahead of the Curve in Radiology AI.
RadAI Slice is your weekly intelligence briefing on the most critical developments at the intersection of radiology and artificial intelligence. Stop searching. Start leading.Subscribe to join 9,800+ radiology professionals tracking the future of imaging AI.
Lastest Issues
The latest developments in Radiology & AI.
Your Weekly Slice of Innovation
Each issue is precisely structured to give you exactly what you need. No fluff, just facts and forward-looking insights.
Recent Industry News
The Latest Research
FDA Approvals Database
Latest News & Trends

ChatGPT Use Soars in Radiology Research Abstracts Since 2023
Radiology research abstracts show a marked rise in LLM-assisted editing since the release of ChatGPT.
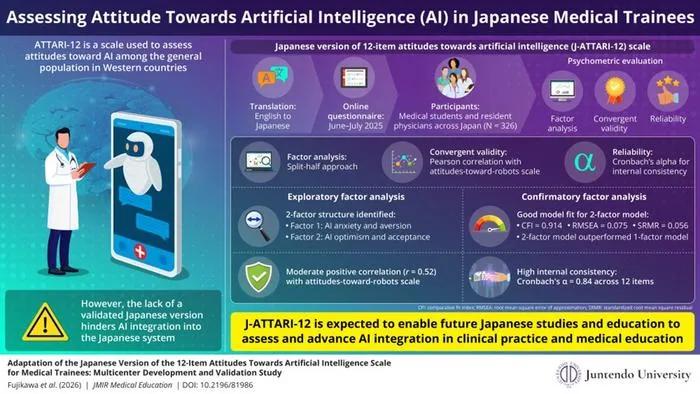
Japanese Medical Trainees' Attitudes Toward AI: New Validated Scale Developed
Researchers validated a Japanese version of the ATTARI-12 scale to measure medical trainees' attitudes toward AI in healthcare.
Real-World Study: AI Improves Breast Cancer Detection in 3D Mammography
AI use in breast radiology increased cancer detection without higher recall rates, according to a 100,000+ case multicenter study.
From the Research Hub
MedicalPatchNet: a patch-based self-explainable AI architecture for chest X-ray classification.
Deep neural networks excel in radiological image classification but frequently suffer from poor interpretability, limiting clinical acceptance. We present MedicalPatchNet, an inherently self-explainable architecture for chest X-ray classification that transparently attributes decisions to distinct image regions. MedicalPatchNet splits images into non-overlapping patches, independently classifies each patch, and aggregates predictions, enabling intuitive visualization of each patch’s diagnostic contribution without post-hoc techniques. Trained on the CheXpert dataset (223,414 images), MedicalPatchNet matches the classification performance (AUROC 0.907 vs. 0.908) of EfficientNetV2-S, while improving interpretability: MedicalPatchNet demonstrates improved interpretability with higher pathology localization accuracy (mean hit-rate 0.485 vs. 0.376 with Grad-CAM) on the CheXlocalize dataset. By providing explicit, reliable explanations accessible even to non-AI experts, MedicalPatchNet mitigates risks associated with shortcut learning, thus improving clinical trust. Our model is publicly available with reproducible training and inference scripts and contributes to safer, explainable AI-assisted diagnostics across medical imaging domains. We make the code publicly available: https://github.com/TruhnLab/MedicalPatchNet
Deep learning-based automated positioning system for maxillary skeletal expander: development and clinical validation.
This study aimed to develop and validate a deep learning-based artificial intelligence (AI) system capable of automatically generating accurate MSE placement plans to enhance clinical efficiency, safety, and consistency. A total of 120 patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion and transverse maxillary deficiency (ages 10–39) were included. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and intraoral scan data were used to construct individualized three-dimensional anatomical coordinate systems. A deep learning model was trained to automatically segment key anatomical structures (e.g., the incisive foramen and transverse palatine suture) and identify essential craniofacial landmarks. The MSE was then automatically positioned within this coordinate system, while a collision detection algorithm ensured appropriate spacing from the palatal mucosa and avoided vital anatomical structures. Model performance was compared with manual placement using metrics such as mean Intersection over Union (mIoU), Avoidance Success Rate (ASR), Mean Radial Error (MRE), Mean Angular Error (MAE), and Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC). The average mIoU of the segmentation network was 0.75. The ASR exceeded 90%, demonstrating effective anatomical avoidance. The automated system achieved an axial MRE of 0.32 ± 0.32 mm, a three-dimensional (3D) Euclidean distance error of 0.69 ± 0.36 mm, and an MAE of 1.84 ± 2.13°, with CCC values above 0.90 for linear and translational directions and between 0.87 and 0.93 for angular directions. These results showed no statistically significant differences from manual placement (<i>P</i> > 0.05).Bland–Altman analysis further showed minimal mean bias between AI and manual planning (translation bias ≤ 0.047 mm; rotation bias within − 0.26° to 1.52°), with 95% limits of agreement for all parameters remaining within clinically acceptable ranges; a mild proportional bias was observed only for yaw (<i>P</i> = 0.013).The automated process required an average of 3 min, significantly faster than the 45–60 minutes typically required for manual planning. The proposed deep learning–based automated MSE positioning system enables accurate and efficient MSE digital planning in a retrospective setting, shows promising clinical potential, and may contribute to more standardized and intelligent orthodontic expansion workflows. This deep learning–driven tool may facilitate standardized MSE placement, shorten treatment planning time, and support clinicians with limited experience, thereby enhancing the safety and efficiency of maxillary skeletal expansion in clinical practice.
Quality versus quantity of training datasets for artificial intelligence-based whole liver segmentation
Artificial intelligence (AI) based segmentation has many medical applications but limited curated datasets challenge model training; this study compares the impact of dataset annotation quality and quantity on whole liver AI segmentation performance. We obtained 3,089 abdominal computed tomography scans with whole-liver contours from MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDA) and a MICCAI challenge. A total of 249 scans were withheld for testing of which 30, MICCAI challenge data, were reserved for external validation. The remaining scans were divided into mixed-curation and highly-curated groups, randomly sampled into sub-datasets of various sizes, and used to train 3D nnU-Net segmentation models. Dice similarity coefficients (DSC), surface DSC with 2mm margins (SD 2mm), the 95th percentile of Hausdorff distance (HD95), and 2D axial slice DSC (Slice DSC) were used to evaluate model performance. The highly curated, 244-scan model (DSC=0.971, SD 2mm=0.958, HD95=2.98mm) performed insignificantly different on 3D evaluation metrics to the mixed-curation 2,840-scan model (DSC=0.971 [p>.999], SD 2mm=0.958 [p>.999], HD95=2.87mm [p>.999]). The 710-scan mixed-curation (Slice DSC=0.929) significantly outperformed the highly curated, 244-scan model (Slice DSC=0.923 [p=0.012]) on the 30 external scans. Highly curated datasets yielded equivalent performance to datasets that were a full order of magnitude larger. The benefits of larger, mixed-curation datasets are evidenced in model generalizability metrics and local improvements. In conclusion, tradeoffs between dataset quality and quantity for model training are nuanced and goal dependent.
From the RadAI FDA Approvals Database
Retia Medical Systems, Inc.
Argos Infinity (Rev. 1.0)
Argos Infinity (Rev. 1.0) by Retia Medical Systems, Inc. is an AI-powered diagnostic tool designed to assist clinicians in analyzing cardiovascular data, aiding in the detection and management of heart-related conditions through advanced computational methods.
Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd.
uMI Panvivo (uMI Panvivo); uMI Panvivo (uMI Panvivo S); uMI Panvivo (uMI Panvivo EX); uMI Panvivo (uMI Panvivo ES)
The uMI Panvivo series by Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co. is a computed emission tomography system used to produce detailed images of the body for diagnostic purposes. It helps clinicians by providing high-quality tomographic images that can be analyzed to detect and diagnose diseases.
Ai4medimaging Medical Solutions S.A.
AI4CMR v2.0
AI4CMR v2.0 is an automated software for processing radiological images. It assists clinicians by improving the analysis of medical images, making diagnosis more efficient and accurate.
The Sharpest Insights, Effortlessly
Save Time
We scour dozens of sources so you don't have to. Get all the essential information in a 5-minute read.
Stay Informed
Never miss a critical update. Understand the trends shaping the future of your practice and research.
Gain an Edge
Be the first to know about the tools and technologies that matter, from clinical practice to academic research.
Ready to Sharpen Your Edge?
Subscribe to join 9,800+ peers who rely on RadAI Slice. Get the essential weekly briefing that empowers you to navigate the future of radiology.
We respect your privacy. Unsubscribe at any time.




