How to Interpret Endoscopic Ultrasounds: 3 Key Techniques
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) combines endoscopy and ultrasound to create detailed images of the digestive tract and nearby organs. This guide will explain what EUS can reveal, why it's used, and how to understand its findings.
What is Endoscopic Ultrasound?
EUS is a minimally invasive procedure where a small ultrasound probe is attached to the end of an endoscope. It allows doctors to obtain high-resolution images of the digestive tract, lymph nodes, and surrounding structures. Let’s explore the specifics of this advanced imaging technique.
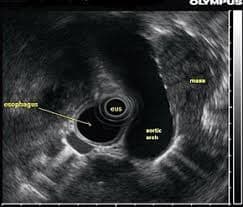
What Can Endoscopic Ultrasound Show?
- Detailed Digestive Tract Imaging: Visualize the layers of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
- Pancreatic and Biliary Evaluation: Clear views of the pancreas, gallbladder, bile ducts, and surrounding structures.
- Lymph Node Imaging: Detailed assessment of lymph nodes near the digestive tract to check for cancer spread or inflammation.
- Tumor Staging: Accurate staging of tumors in the digestive system, which helps in treatment planning.
- Guidance for Procedures: Enables precise guidance for biopsies, fine-needle aspirations, and therapeutic interventions.
Why Might You Need an Endoscopic Ultrasound?
- Unexplained Abdominal Pain: Investigate the cause of abdominal discomfort, particularly related to the pancreas and bile ducts.
- Abnormal CT or MRI Scans: Further assess abnormalities found on other imaging studies of the digestive system.
- Suspected Pancreatic or Biliary Disease: Evaluate suspected conditions such as pancreatitis, gallstones, and tumors.
- Cancer Diagnosis and Staging: Determine the extent of cancer in the digestive tract and surrounding tissues.
- Therapeutic Procedures: Guide interventions like draining cysts, delivering medication, or performing ablation therapy.
How is an Endoscopic Ultrasound Performed?
The EUS procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible endoscope with a small ultrasound probe at its tip through the mouth or rectum, depending on the area of interest. Here's a step-by-step overview:
- Preparation: You'll typically be asked to fast for several hours before the procedure. Sedation or anesthesia is often used to ensure comfort.
- Insertion: The endoscope is gently inserted through your mouth or rectum and advanced to the target area within the digestive tract.
- Ultrasound Imaging: The ultrasound probe transmits sound waves to create real-time images of the targeted organs and tissues.
- Biopsy (if needed): If any abnormal areas are identified, a fine needle can be passed through the endoscope to obtain a tissue sample for biopsy.
- Procedure Completion: Once completed, the endoscope is carefully removed. You'll be monitored as you recover from the sedation.
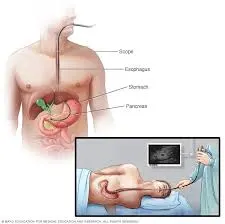
The procedure generally takes between 30 minutes to an hour, depending on complexity. Most patients can return home the same day after a brief recovery.
How to Interpret Endoscopic Ultrasound Results
Understanding EUS results is key to effective patient care. Here's an overview of common methods to help you interpret the findings.
1. Utilizing X-ray Interpreter
X-ray Interpreter now analyzes ultrasound images with its AI-driven analysis. Here’s how to use it:
- Registration: Sign up on X-ray Interpreter to use our AI for EUS analysis.
- Uploading Ultrasounds: Upload your endoscopic ultrasound images.
- Reviewing Interpretation: Receive the AI-generated interpretation, including a report.
- Consultation: Always consult with your physician for comprehensive diagnosis.
Check our get started guide for more details.
2. Using ChatGPT Plus
ChatGPT Plus, with its advanced GPT-4V model, can assist in analyzing ultrasound images:
- Subscription: Subscribe to ChatGPT Plus for advanced analysis.
- Uploading Ultrasounds: Upload your ultrasound images on the OpenAI platform.
- Request Analysis: Ask the AI to interpret your ultrasound images and give you a report.
- Review and Validate: Review the results and confirm its accuracy with a healthcare professional.
Find out more in our blog on using ChatGPT Plus for medical image interpretation.
Alternatively, as several other AI models with vision capabilities emerge, you can also try other models, such as Grok by xAI, Claude by Anthropic, Gemini by Google Deepmind.
3. Understanding the Basics Yourself
While not a substitute for medical expertise, learning some basics can help you better understand the results and prepare for discussions with your doctor.
- Learn Anatomy: Familiarize yourself with the basic anatomy of the digestive tract, pancreas, and biliary system.
- Read Simple Guides: Use online resources to understand common findings in EUS.
- Ask Questions: Note any unfamiliar terms and ask your healthcare provider during follow-up appointments.
- Seek Expert Guidance: Always validate your understanding with a medical professional.
Comparing the Different Approaches
Let's compare different methods for interpreting endoscopic ultrasounds:
| Criteria | X-ray Interpreter | ChatGPT Plus | Self-Reading |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High (AI-based)1 | High (AI-based)1 | Varies (Skill-dependent) |
| Ease of Use | Easy | Moderate | Challenging |
| Cost | Starting from $2.50 per image | $20 per month | Free (excluding educational costs) |
| Time Efficiency | Fast | Moderate to Fast | Slow to Moderate |
| Learning Curve | Low | Low to Moderate | High |
| Additional Resources | Provided | Partially Provided (through OpenAI) | Self-sourced |
Each method has advantages. AI-driven options are fast and precise, while basic understanding aids in better patient-doctor communication.
Conclusion
Endoscopic ultrasound is a powerful tool for diagnosing and managing various digestive conditions. This guide has introduced you to the use of EUS, the images it produces, and ways you can better understand your results through AI tools and self-education.
When choosing a method, consider your needs, understanding level, and available resources. Always follow privacy standards and seek expert medical validation.