How to Interpret Thoracic Spine MRIs 3 Essential Techniques
Understanding thoracic spine MRIs is crucial for diagnosing and treating spinal conditions effectively. This guide introduces you to the MRI's advantages over X-rays and explains three key techniques for interpreting these detailed images.
Understanding Thoracic Spine MRIs
A thoracic spine MRI provides a comprehensive view of the upper and mid-back, offering detailed images of bones, soft tissues, nerves, and the spinal cord. This section outlines what thoracic spine MRIs are and their advantages for diagnosing various conditions.
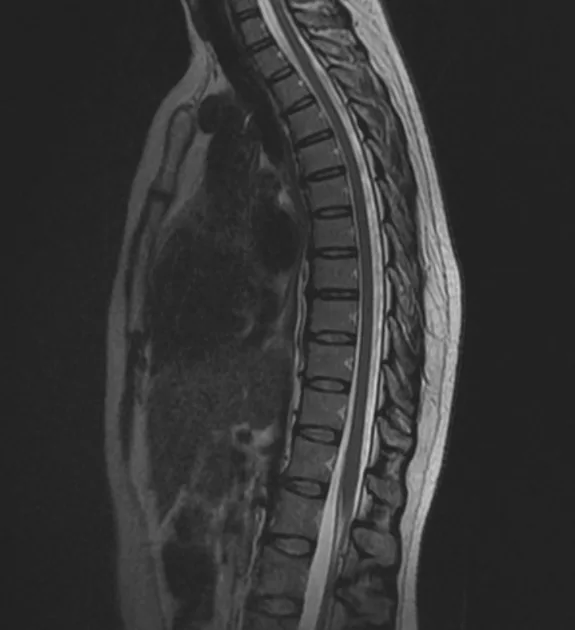
What Do Thoracic Spine MRIs Show?
- Soft Tissue Detail: Superior imaging of muscles, ligaments, and the spinal cord.
- Nerve Pathways: Clear visualization of nerve roots, useful in diagnosing nerve impingement or damage.
- Bone Marrow Changes: Detects changes within the bone marrow not visible on X-rays.
- Disease Detection: More effective in identifying infections and tumors.
When Will You Get One?
- Persistent Upper or Mid-back Pain: Especially if not adequately explained by an X-ray.
- Neurological Symptoms: Such as tingling or weakness indicating nerve involvement.
- Pre-surgical Planning: Provides a detailed anatomy for surgical planning.
- Monitoring Disease Progression: Ideal for assessing changes over time in chronic conditions.
Techniques to Interpret Thoracic Spine MRIs
Interpreting thoracic spine MRIs involves a deeper understanding of advanced imaging techniques. Here are three techniques for professionals at different levels of expertise.
1. Utilizing X-ray Interpreter
X-ray Interpreter now extends its AI-driven analysis to MRI images. The process ensures precision:
- Registration: Register on X-ray Interpreter to access AI analysis for MRIs.
- Uploading MRIs: Upload your thoracic spine MRI images.
- Reviewing Interpretation: Receive the AI-generated interpretation and download your report.
- Professional Consultation: Always advisable to consult with medical professionals for comprehensive understanding.
Please check out our get started guide.
2. Using ChatGPT Plus
ChatGPT Plus now supports MRI image analysis with its latest GPT-4V model, offering detailed and interactive insights:
- Subscription: Subscribe to ChatGPT Plus for advanced image analysis features.
- Uploading MRIs: Interface with GPT-4V on OpenAI to upload your MRI images.
- Requesting Analysis: Engage with the model for a thorough analysis.
- Review and Confirmation: Assess and refine the analysis as needed.
- Professional Validation: Validation by medical experts is recommended.
Read more on our post about using ChatGPT Plus for MRI interpretation.
Alternatively, as several other AI models with vision capabilities emerge, you can also try other models, such as Grok by xAI, Claude by Anthropic, Gemini by Google Deepmind.
3. Mastering MRI Interpretation Yourself
For healthcare professionals aiming to enhance their MRI reading skills, self-learning is invaluable:
- Education: Pursue advanced training in MRI interpretation.
- Practice: Regular practice under expert guidance.
- Resources: Utilize advanced imaging books and online courses.
- Feedback: Seek feedback to refine skills.
- Continuous Learning: Engage in ongoing education to stay current with imaging techniques.
Recommended Resources for Self-Learning:
-
Normal thoracic spine MRI - Radiopaedia: This case study provides an example of a normal thoracic spine MRI, highlighting the typical appearance of the thoracic vertebrae, spinal cord, and surrounding tissues.
-
A Patient's Guide: How To Navigate Your Spine MRI - DocPanel: Offers practical tips and expert advice on understanding your spine MRI report, helping patients navigate through complex medical terminology and findings.
-
Understanding an MRI of the Normal Thoracic Spine - Neck and Back: This video tutorial is designed to help primary care physicians and specialists learn how to read and interpret a normal thoracic spine MRI.
Comparative Analysis
Choosing the right technique for interpreting thoracic spine MRIs is vital for accurate diagnosis. This section compares the three methods:
| Criteria | X-ray Interpreter | ChatGPT Plus | Self-Reading |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High (AI-based)1 | High (AI-based)1 | Varies (Skill-dependent) |
| Ease of Use | Easy | Moderate | Challenging |
| Cost | Starting from $2.50 per image | $20 per month | Free (excluding educational costs) |
| Time Efficiency | Fast | Moderate to Fast | Slow to Moderate |
| Learning Curve | Low | Low to Moderate | High |
| Additional Resources | Provided | Partially Provided (through OpenAI) | Self-sourced |
Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, with AI options providing rapid and precise interpretations, while self-reading encourages in-depth learning for medical professionals.
Conclusion
Thoracic spine MRI interpretation is critical for diagnosing complex spinal conditions. This guide presents three techniques suited to different professional needs and skill levels. AI methods offer quick, precise interpretations, while self-learning is geared towards those seeking in-depth knowledge.
When selecting a technique, consider your level of expertise, the need for timely interpretation, and the resources available. Ethical and legal standards must always be maintained to ensure patient safety and confidentiality.
Related Articles
- How to Interpret Lumbar Spine MRIs
- How to Interpret Lumbar X-rays
- How to Interpret Thoracic X-rays
- How to Interpret Spine CT Scans
Resources and Further Learning
For further exploration and understanding of thoracic spine MRI interpretation, consider the following resources:
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the Spine and Brain - Johns Hopkins Medicine: This resource provides a comprehensive overview of MRI procedures, including detailed descriptions of spine and brain MRIs, their uses, and what patients can expect during the process.
-
Thoracic Spine Protocol (MRI) - Radiopaedia: Offers a detailed protocol for thoracic spine MRI, including indications, patient positioning, and technical parameters, making it a valuable guide for healthcare professionals.
-
MRI of the Thoracic Spine – Radiology In Plain English: Provides a thorough explanation of thoracic spine MRI, including the procedure, indications, common findings, and treatment options based on MRI results.