How to interpret shoulder X-rays: 3 Key Techniques
Introduction
Interpreting shoulder X-rays is an essential skill in orthopedics and sports medicine, as it plays a pivotal role in diagnosing and managing musculoskeletal issues. This guide is designed to introduce readers to shoulder X-rays and outline three key techniques for their interpretation.
Understanding Shoulder X-rays
Shoulder X-ray is a prevalent imaging test that provides detailed views of the shoulder region, including bones, joints, and surrounding soft tissues. This section will guide you through the basics of shoulder X-rays and their applications.
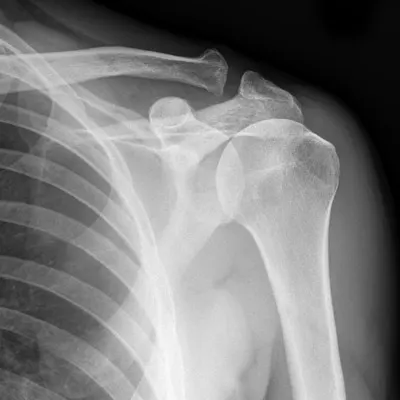
What Do Shoulder X-rays Show?
- Bone Conditions: Detection and monitoring of fractures, arthritis, and bone degeneration.
- Joint Analysis: Assessment of the shoulder joint, including the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints.
- Soft Tissue Conditions: Evaluation of tendons, muscles, and other soft tissues around the shoulder.
- Dislocations: Identification of dislocations and their severity in the shoulder region.
When Will You Get One?
- Symptom Investigation: Persistent shoulder pain, limited mobility, or injury to the shoulder.
- Postoperative Evaluation: Monitoring the status of surgical interventions in the shoulder area.
- Sports-related Assessments: Evaluation of sports injuries and planning for rehabilitation.
- Occupational Health Screenings: Checking for chronic shoulder issues in workers performing repetitive tasks.
Techniques to Interpret Shoulder X-rays
Interpreting shoulder X-rays requires a combination of anatomical knowledge and practical expertise. Below, we explore three techniques that cater to varying levels of skill and needs.
1. Utilizing X-ray Interpreter
X-ray Interpreter offers a streamlined approach to analyzing shoulder X-rays through advanced AI algorithms. Here’s how you can benefit from this tool:
- Registration: Sign up on X-ray Interpreter for accessing AI-based analysis tools.
- Uploading X-rays: Upload your shoulder X-ray images to the platform.
- Reviewing Interpretation: Analyze the AI-generated interpretation and download the detailed report.
- Professional Consultation: Consult with orthopedic experts for further understanding of the AI analysis.
Please check out our get started guide.
2. Using ChatGPT Plus
ChatGPT Plus, using the GPT-4V model, offers a unique approach to analyze shoulder X-ray images. The process includes:
- Subscription: Gain access to GPT-4V for image analysis by subscribing to ChatGPT Plus.
- Uploading X-rays: Use the OpenAI platform to upload shoulder X-ray images.
- Requesting Analysis: Ask for an analysis of the images through conversational prompts.
- Iterative Review: Refine the analysis as needed and validate it with medical experts.
Read more about this process in our article.
Alternatively, as several other AI models with vision capabilities emerge, you can also try other models, such as Grok by xAI, Claude by Anthropic, Gemini by Google Deepmind.
3. Self-Interpreting Shoulder X-rays
Self-interpretation is ideal for medical professionals with a specific focus on orthopedics or sports medicine. It involves:
- Educational Foundation: Acquiring knowledge about shoulder anatomy and common pathologies.
- Practical Experience: Gaining experience by interpreting various shoulder X-ray images.
- Resource Utilization: Accessing specialized books, online courses, and journals.
- Expert Feedback: Receiving guidance and feedback from experienced orthopedic radiologists.
- Continuous Learning: Keeping up-to-date with the latest trends and techniques in shoulder X-ray interpretation.
Suggested Resources for Self-Interpreting:
-
Geeky Medics - Shoulder X-ray Interpretation
- Offers a comprehensive guide to interpreting shoulder X-rays in an emergency department context, focusing on the glenohumeral joint, clavicle, and acromioclavicular joint. It provides detailed steps for confirming patient details, acquiring necessary views, and a structured approach to interpretation.
-
Don't Forget the Bubbles - Shoulder X-ray Interpretation
- A resource that covers the essentials of pediatric shoulder X-ray interpretation. It includes guidelines for ensuring an adequate X-ray, examining bones and joints, understanding ossification centers in children, and checking for foreign bodies and subcutaneous emphysema.
-
Radiopaedia - Shoulder Radiograph (An Approach)
- This article provides an approach to shoulder radiographs commonly seen in emergency departments. It emphasizes a systematic review, including assessment of soft tissue areas, cortical margins, trabecular patterns, bony alignment, joint congruency, and common pathologies like anterior shoulder dislocation, clavicle fracture, and acromioclavicular joint injury.
These resources offer diverse learning materials for enhancing skills and knowledge in interpreting shoulder X-rays, catering to different expertise levels.
Comparative Analysis
Choosing the right technique for interpreting shoulder X-rays is crucial for effective diagnosis and management. This section compares the three techniques: X-ray Interpreter, ChatGPT Plus, and Self-Interpreting, based on accuracy, user-friendliness, cost, time efficiency, learning curve, and availability of resources.
| Criteria | X-ray Interpreter | ChatGPT Plus | Self-Reading |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Mostly High (AI-based)1 | Mostly High (AI-based)1 | Varies (Skill-dependent) |
| Ease of Use | Easy | Moderate | Challenging |
| Cost | Starting from $2.50 per image | $20 per month | Free (excluding educational costs) |
| Time Efficiency | Fast | Moderate to Fast | Slow to Moderate |
| Learning Curve | Low | Low to Moderate | High |
| Additional Resources | Provided | Partially Provided (through OpenAI) | Self-sourced |
The table helps to quickly assess each method's strengths and limitations, facilitating an informed choice based on individual needs and expertise.
Conclusion
Interpreting shoulder X-rays is a vital component in orthopedics and sports medicine, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. This guide presented three techniques for shoulder X-ray interpretation: X-ray Interpreter, ChatGPT Plus, and self-interpretation, each addressing different expertise levels and requirements.
AI-based methods like X-ray Interpreter and ChatGPT Plus offer swift and precise interpretations, ideal for immediate insights. Self-interpretation, while more challenging, provides an opportunity for in-depth learning and skill enhancement for medical professionals.
This guide also included resources for further education and skill development in shoulder X-ray interpretation. Staying abreast of the latest advancements in imaging technology and interpretation methods is key to delivering high-quality patient care in orthopedics and sports medicine.
This guide serves as an informative resource for those exploring shoulder X-ray interpretation, helping them navigate this important aspect of musculoskeletal diagnostics. The choice of interpretation technique should align with personal preferences, professional objectives, and specific clinical scenarios.
Related Articles
Resources and Further Learning
For those interested in expanding their knowledge in shoulder X-ray interpretation, here are some informative resources:
-
EMRad: Radiologic Approach to the Traumatic Shoulder
- A series by EMRad focused on providing approaches to commonly ordered radiology studies in emergency departments, including the shoulder. This resource offers a standard approach for interpreting traumatic shoulder x-rays and identifies clinical scenarios where additional views might improve diagnosis.
-
X-ray Vision - Shoulders and Elbows — Taming the SRU
- This resource covers the radiography of the shoulder, emphasizing the indications for different types of shoulder pain and the limitations of plain films in diagnosing certain conditions.
-
- An in-depth module on shoulder X-rays, mainly used for diagnosing fractures. It covers key topics such as proximal humeral fracture, shoulder dislocation, Bankart lesion, osteoarthritis, and more.
These resources offer varied perspectives and detailed insights into the interpretation of shoulder X-rays, catering to different levels of expertise.