How to Interpret Echocardiograms: 3 Key Methods
An echocardiogram, often called an "echo," is a crucial diagnostic tool that uses sound waves to create moving pictures of your heart. This guide explains what an echocardiogram reveals, why it's used, and how to interpret its findings effectively.
What is an Echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram is a non-invasive imaging test that offers real-time images of the heart's chambers, valves, and surrounding blood vessels. Unlike X-rays, it utilizes sound waves, making it a safe and painless procedure. Let's explore what this technique involves and what it shows.
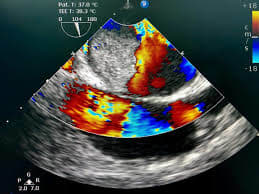
What Can an Echocardiogram Show?
- Detailed Heart Imaging: Clear visualization of heart chambers, valves, and the pericardium.
- Function Assessment: Measures heart muscle strength, valve function, and blood flow.
- Abnormality Identification: Helps detect structural issues, valve problems, and blood clots.
- Real-time Imaging: Allows doctors to see the heart's contractions in real-time.
- Guidance for Procedures: Can guide catheter-based interventions and other cardiac procedures.
Why Might You Need an Echocardiogram?
- Chest Pain: To help identify the cause of unexplained chest discomfort.
- Shortness of Breath: When there are suspected heart function issues.
- Heart Murmurs: To examine heart valves and chamber function.
- Known Heart Conditions: To monitor the progression of heart diseases.
- Pre-Operative Assessment: To evaluate heart function before surgery.
How is an Echocardiogram Performed?
An echocardiogram is a non-invasive procedure that is generally painless and quick. Here’s what typically happens:
- Preparation: You will be asked to undress from the waist up and wear a gown. You'll lie on your back or left side on an examination table.
- Electrode Placement: Small, sticky patches called electrodes are placed on your chest to monitor your heart’s electrical activity.
- Gel Application: A clear, water-based gel is applied to your chest. This helps the transducer make good contact with your skin.
- Transducer Movement: A handheld device called a transducer is moved across your chest. The transducer sends out sound waves that create images of your heart.
- Image Acquisition: The ultrasound machine captures real-time images of your heart, including the chambers, valves, and blood flow.
- Various Views: The technician may move the transducer to different locations to obtain various views of your heart.
- Duration: A standard echocardiogram usually takes about 30 to 60 minutes.
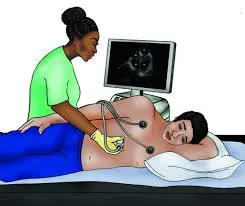
The procedure is painless, and you can usually return to your normal activities right away.
How to Interpret Echocardiogram Results
Understanding your echocardiogram results is key to managing your heart health. Here are several methods to help interpret the findings.
1. Utilizing X-ray Interpreter
X-ray Interpreter provides AI-driven analysis for echocardiogram images. Here’s how to use it:
- Registration: Sign up on X-ray Interpreter to utilize our AI for analysis.
- Uploading Echocardiograms: Upload your echocardiogram images.
- Reviewing Interpretation: Receive the AI-generated interpretation, including a report.
- Consultation: Always consult with your physician for comprehensive diagnosis.
Check our get started guide for more details.
2. Using ChatGPT Plus
ChatGPT Plus, powered by the advanced GPT-4V model, can assist in analyzing echocardiogram images:
- Subscription: Subscribe to ChatGPT Plus for advanced analysis.
- Uploading Echocardiograms: Upload your echocardiogram images on the OpenAI platform.
- Request Analysis: Ask the AI to interpret your echocardiogram images and provide a report.
- Review and Validate: Review the results and confirm their accuracy with a healthcare professional.
Find out more in our blog on using ChatGPT Plus for medical image interpretation.
Alternatively, as several other AI models with vision capabilities emerge, you can also try other models, such as Grok by xAI, Claude by Anthropic, Gemini by Google Deepmind.
3. Understanding the Basics Yourself
While it is not a substitute for professional medical advice, understanding some basics can help you better comprehend the results and prepare questions for your doctor.
- Learn Heart Anatomy: Familiarize yourself with the basic anatomy of the heart.
- Read Simple Guides: Many online resources explain common findings in echocardiograms.
- Ask Questions: Note any unfamiliar terms and ask your healthcare provider during follow-up.
- Seek Expert Guidance: Always validate your understanding with a medical professional.
Comparing the Different Approaches
Let's compare the methods for interpreting echocardiograms:
| Criteria | X-ray Interpreter | ChatGPT Plus | Self-Reading |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High (AI-based)1 | High (AI-based)1 | Varies (Skill-dependent) |
| Ease of Use | Easy | Moderate | Challenging |
| Cost | Starting from $2.50 per image | $20 per month | Free (excluding educational costs) |
| Time Efficiency | Fast | Moderate to Fast | Slow to Moderate |
| Learning Curve | Low | Low to Moderate | High |
| Additional Resources | Provided | Partially Provided (through OpenAI) | Self-sourced |
Each method offers unique advantages. AI-driven options are fast and precise, while basic understanding enables better patient-doctor interaction.
Conclusion
Echocardiograms are vital for diagnosing heart conditions and understanding heart health. This guide has explored the use of echocardiography, the images it produces, and how you can better understand your results using AI tools and self-education.
When choosing a method, consider your specific needs, desired level of understanding, and resources available. Always prioritize privacy and seek professional medical guidance.
Related Articles
- How To Interpret Cardiac CT Scans
- How To Interpret Cardiac MRIs
- How To Interpret Chest X-Rays
- How To Interpret Vascular Ultrasounds