What is the Difference Between Pleural Effusion and Pulmonary Edema?
When it comes to breathing difficulties, two conditions often come to mind: pulmonary edema and pleural effusion. These terms might sound complex, but understanding them can be life-saving. Let’s explore these conditions, their causes, symptoms, diagnoses, and treatments, using simple language to make it clear.
What is Pulmonary Edema?
Pulmonary edema is a condition where fluid collects in the lung's air sacs, called alveoli. These tiny sacs are where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide in the blood. When they fill with fluid, it becomes harder to breathe because the lungs can't take in enough oxygen.
Causes of Pulmonary Edema
Pulmonary edema is often caused by heart problems. When the heart fails to pump blood efficiently, blood backs up into the veins that carry blood through the lungs. This increases pressure in these blood vessels, pushing fluid into the alveoli.
However, heart issues aren't the only cause. Other causes include:
- High Altitude: Sometimes, being at high altitudes can cause fluid to leak into the lungs.
- Infections: Severe infections, like pneumonia, can lead to fluid buildup.
- Inhalation of Toxins: Breathing in harmful substances like smoke or chemicals can damage the lungs, causing fluid accumulation.
- Kidney Failure: This can cause fluid retention, leading to pulmonary edema.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Edema
The symptoms of pulmonary edema can be sudden or gradual and include:
- Shortness of Breath: This can be sudden and severe, especially if lying down.
- Coughing: Producing frothy, possibly blood-tinged sputum.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound when breathing.
- Rapid Breathing: Feeling like you can't catch your breath.
- Chest Pain: Sometimes, a feeling of tightness in the chest.
Diagnosing Pulmonary Edema
If a doctor suspects pulmonary edema, they will perform several tests, including:
- Chest X-ray: To see the fluid in the lungs.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To check for heart problems.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart.
- Blood Tests: To check for conditions like kidney failure or infections.
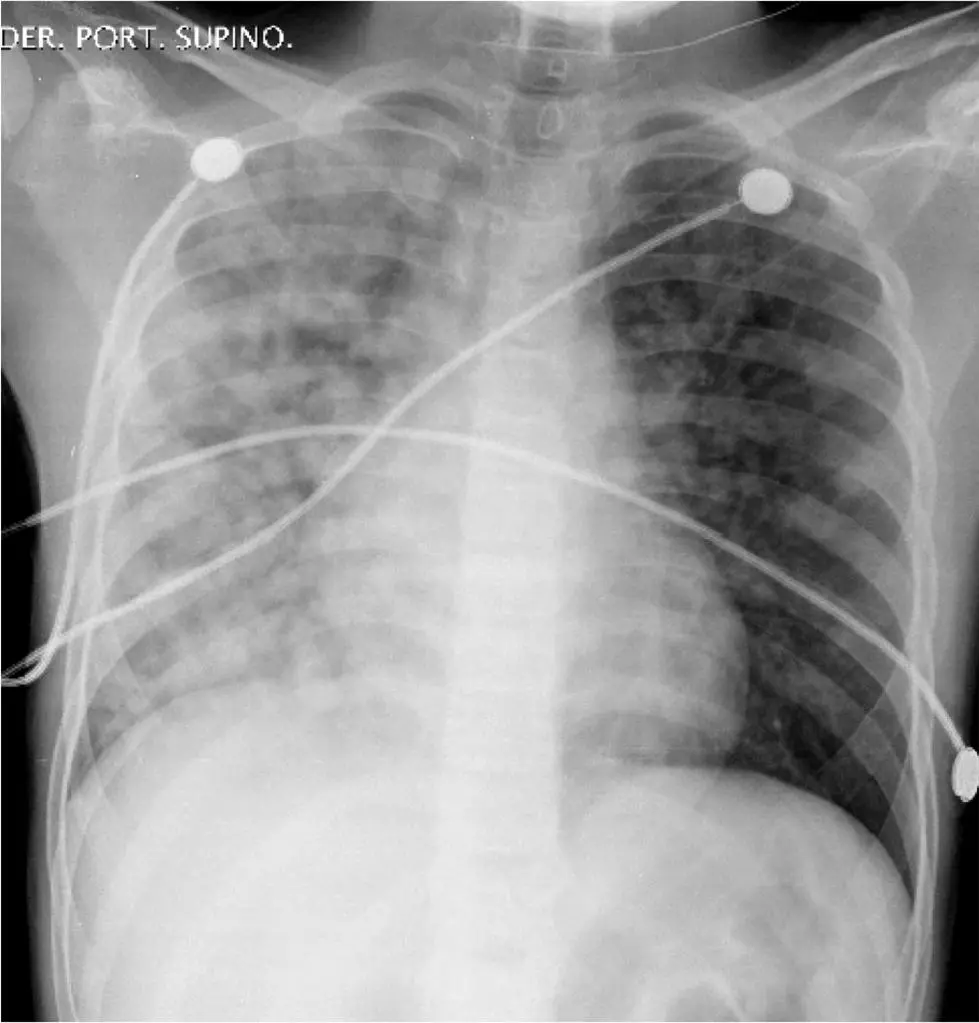
Treating Pulmonary Edema
Treatment for pulmonary edema depends on the cause but may include:
- Oxygen Therapy: To help you breathe easier.
- Diuretics: Medications that help remove excess fluid from your body.
- Medications for Heart: To help the heart pump more effectively.
- Treating Underlying Cause: Such as antibiotics for infections or addressing kidney issues.
What is Pleural Effusion?
Pleural effusion is different. This condition occurs when excess fluid builds up in the pleural space, which is the area between the lungs and the chest wall. Normally, this space has a small amount of fluid to help the lungs move smoothly during breathing. However, too much fluid can compress the lungs and make breathing difficult.
Causes of Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion can be caused by many conditions, including:
- Congestive Heart Failure: The most common cause, where the heart doesn't pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup.
- Liver Disease: Conditions like cirrhosis can cause fluid to leak into the pleural space.
- Kidney Disease: Can lead to fluid retention and pleural effusion.
- Infections: Such as pneumonia or tuberculosis.
- Cancer: Tumors can block lymphatic drainage, causing fluid buildup.
- Pulmonary Embolism: A blood clot in the lung can lead to pleural effusion.
Symptoms of Pleural Effusion
The symptoms of pleural effusion can include:
- Shortness of Breath: Especially during physical activity.
- Chest Pain: Usually sharp and worsens with deep breaths or coughing.
- Cough: Persistent and dry.
- Decreased Lung Expansion: The affected side of the chest may not expand as much when breathing.
Diagnosing Pleural Effusion
To diagnose pleural effusion, doctors use:
- Chest X-ray: To detect fluid in the pleural space.
- Ultrasound: To guide fluid removal.
- CT Scan: To get detailed images of the chest.
- Thoracentesis: A procedure where fluid is removed from the pleural space for analysis.
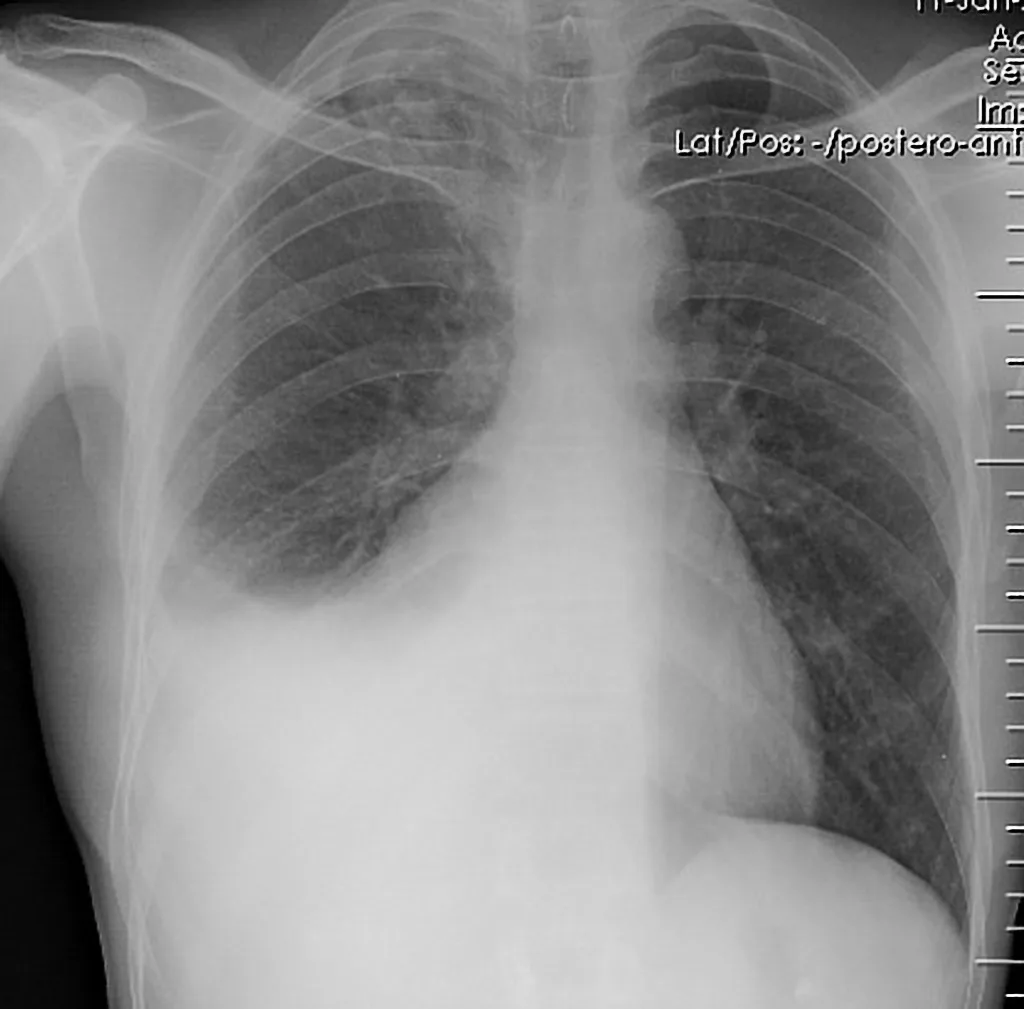
Treating Pleural Effusion
Treatment for pleural effusion depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Thoracentesis: To drain the fluid and relieve symptoms.
- Medications: Such as diuretics for heart failure or antibiotics for infections.
- Surgery: In severe cases, to remove part of the pleura or insert a shunt to drain fluid.
Key Differences Between Pulmonary Edema and Pleural Effusion
While both conditions involve fluid buildup and cause breathing difficulties, they differ significantly:
-
Location of Fluid:
- Pulmonary edema: Fluid is in the lung's air sacs (alveoli).
- Pleural effusion: Fluid is in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall.
-
Common Causes:
- Pulmonary edema: Often due to heart problems, but can also be caused by infections, toxins, or kidney failure.
- Pleural effusion: Can result from heart failure, liver or kidney disease, infections, cancer, or pulmonary embolism.
-
Symptoms:
- Pulmonary edema: Includes shortness of breath, coughing up frothy sputum, and wheezing.
- Pleural effusion: Involves chest pain, shortness of breath, and decreased lung expansion on the affected side.
-
Diagnosis:
- Pulmonary edema: Diagnosed with chest X-rays, ECGs, echocardiograms, and blood tests.
- Pleural effusion: Diagnosed with chest X-rays, ultrasounds, CT scans, and thoracentesis.
-
Treatment:
- Pulmonary edema: Treated with oxygen therapy, diuretics, medications to support heart function, and addressing the underlying cause.
- Pleural effusion: Treated with thoracentesis, medications, and sometimes surgery, depending on the cause.
Understanding the Impact of These Conditions
Both pulmonary edema and pleural effusion are serious conditions that require medical attention. They can significantly impact quality of life and may lead to further health complications if not treated promptly.
Pulmonary Edema
The rapid onset of symptoms can be frightening and life-threatening. Prompt treatment is crucial to reduce fluid buildup and improve breathing. Long-term management may involve lifestyle changes and medications to address underlying heart or kidney issues.
Pleural Effusion
This condition can be more gradual but still requires timely intervention. Regular monitoring and treating the underlying cause can help prevent recurrence. In some cases, chronic pleural effusions may require ongoing medical procedures to manage fluid buildup.
Personal Stories and Case Studies
To better understand these conditions, let’s look at some real-life examples.
Case Study 1: John’s Experience with Pulmonary Edema
John, a 65-year-old retired teacher, suddenly found himself gasping for breath one night. His wife called an ambulance, and John was rushed to the hospital. Doctors diagnosed him with pulmonary edema caused by undiagnosed heart failure. After receiving oxygen therapy and medications to reduce fluid, John’s breathing improved. He now takes medications to manage his heart condition and has regular check-ups to monitor his health.
Case Study 2: Maria’s Battle with Pleural Effusion
Maria, a 55-year-old woman, had been feeling increasingly short of breath and noticed a sharp pain in her chest whenever she took deep breaths. After visiting her doctor, she was diagnosed with pleural effusion caused by a pulmonary embolism. Maria underwent a thoracentesis to drain the fluid, which provided immediate relief. She was also treated for the blood clot and now takes medication to prevent further clots.
Preventing Pulmonary Edema and Pleural Effusion
While not all cases can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
For Pulmonary Edema
- Manage Heart Health: Regular check-ups, a healthy diet, and exercise can help keep your heart healthy.
- Avoid Toxins: Limit exposure to harmful substances like smoke and chemicals.
- Monitor Health Conditions: Keep conditions like kidney disease and infections under control.
For Pleural Effusion
- Address Underlying Health Issues: Manage conditions like heart failure, liver disease, and kidney disease.
- Prevent Infections: Take steps to avoid respiratory infections, such as getting vaccinated and practicing good hygiene.
- Monitor Symptoms: If you have a condition that increases your risk, pay attention to symptoms and seek medical advice early.
Before You Go...
Understanding pulmonary edema and pleural effusion is crucial, but having the right tools can make a significant difference in managing these conditions.
At X-ray Interpreter, we specialize in providing accurate and timely analysis of your X-rays and other imaging results. Our advanced AI technology helps you understand complex medical images, offering insights that can guide your treatment decisions.
Imagine having a powerful tool that deciphers your medical images with precision, uncovering the hidden details that can impact your health.
Whether you're grappling with symptoms of pulmonary edema, pleural effusion, or any other concern, our platform ensures you receive clear, concise explanations of your radiology results.
Don't let medical jargon and complex images leave you in the dark. Empower yourself with the knowledge you need to take control of your health.
Visit X-ray Interpreter today and discover how we can assist you in interpreting your medical images, providing clarity and peace of mind. Your health is our priority!