Understanding Exophytic Growths
When doctors use the term "exophytic," they're describing something that grows outward from a surface. Think of it like a tree branch growing outward from the trunk, rather than growing within the trunk itself. This term is commonly used in medical settings to describe various types of growths that project from organs or tissues.
Types of Common Locations
| Body System | Common Growths | Typical Characteristics | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skin | Warts, Tags, Moles | Visible, Often painless | Usually low |
| Respiratory | Polyps, Nodules | May affect breathing | Moderate |
| Urinary | Kidney masses, Bladder polyps | May cause bleeding | Variable |
| Digestive | Colon polyps, Stomach lesions | Can be symptomless | Moderate |
| Reproductive | Fibroids, Cysts | May cause discomfort | Usually low |
Watch for these quick warning signs:
- Rapid growth
- Unexpected pain
- Color changes
- Bleeding
- New symptoms
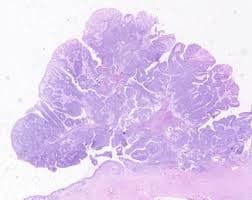
The Importance of Medical Imaging in Diagnosis and Monitoring
Medical imaging plays a crucial role in managing exophytic conditions, serving as the cornerstone of both initial diagnosis and ongoing monitoring. Modern imaging techniques have revolutionized how healthcare providers approach these growths, offering unprecedented insight into their structure, composition, and relationship with surrounding tissues. When a patient presents with symptoms suggesting an exophytic growth, healthcare providers typically begin with basic imaging studies and may progress to more sophisticated techniques based on initial findings. The interpretation of these images, which can now be aided by AI tools like X-ray Interpreter, helps healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment approaches and monitoring strategies.
Imaging Characteristics
| Imaging Type | What It Shows | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray | Basic outline, calcifications | Quick, affordable | Limited detail |
| CT Scan | 3D structure, density | Excellent detail | Radiation exposure |
| MRI | Soft tissue detail, fluid content | No radiation | Time-consuming |
| Ultrasound | Real-time movement, blood flow | Safe, dynamic | Operator dependent |
| PET Scan | Metabolic activity | Shows function | Expensive |
Stages of Growth:
- Initial appearance
- Early development
- Established growth
- Advanced stage
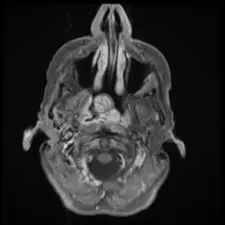
Treatment Approaches and Success Rates
The management of exophytic growths represents a complex medical decision-making process that must take into account multiple factors including the patient's age, overall health status, the location and characteristics of the growth, and the potential risks versus benefits of various treatment options. Healthcare providers typically develop individualized treatment plans that may evolve over time based on the response to initial interventions and any changes in the growth's characteristics or the patient's condition. This patient-centered approach ensures that treatment strategies align with both medical best practices and the patient's personal preferences and goals.
| Treatment Type | Success Rate | Recovery Time | Cost Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monitoring only | N/A | N/A | Low |
| Medication | 40-75% | Weeks to months | Moderate |
| Minor surgery | 85-95% | Days to weeks | Moderate |
| Major surgery | 90-98% | Weeks to months | High |
| Combined therapy | 75-95% | Variable | High |
A few quick prevention tips:
- ✓ Regular screenings
- ✓ Healthy lifestyle
- ✓ Sun protection
- ✓ Prompt attention to changes
Impact on Quality of Life and Long-term Outlook
Living with an exophytic condition requires a balanced approach to health management and lifestyle adjustments. Patients often find that while the initial diagnosis may be concerning, proper medical care and regular monitoring can lead to successful management of their condition. The psychological impact should not be underestimated, and many patients benefit from a combination of medical care and emotional support. Understanding the natural history of these growths, maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, and following recommended monitoring protocols all contribute to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
| Life Aspect | Potential Impact | Management Strategies | Support Needed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical | Activity limitations | Modified exercise | Medical team |
| Social | Appearance concerns | Support groups | Friends/Family |
| Emotional | Anxiety/worry | Counseling | Mental health |
| Professional | Time off needs | Workplace adjustments | HR support |
Key Monitoring Points:
- Regular imaging
- Symptom tracking
- Growth measurements
- Quality of life assessment
Documentation and Personal Health Records
Keeping detailed records of your exophytic condition is crucial for optimal healthcare management. A well-organized documentation system helps both you and your healthcare providers track changes and make informed decisions.
| Record Type | What to Include | Frequency | Format |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Pain levels, changes | Daily/Weekly | Digital/Paper log |
| Measurements | Size, appearance | Monthly | Photo + measurements |
| Test Results | Lab work, imaging | Per occurrence | Medical records |
| Medications | Dosage, effects | Ongoing | Medication diary |
Quick tip: Use your smartphone to photograph visible growths regularly, keeping a visual timeline of any changes.
Support Resources and Patient Communities
The journey of managing an exophytic condition doesn't have to be a solitary one. A robust support network can significantly improve both treatment outcomes and emotional well-being. Modern healthcare approaches recognize the value of comprehensive support systems that extend beyond traditional medical care.
Professional Support Network:
- Primary Care Provider
- Specialists
- Medical Imaging Technologists
- Mental Health Professionals
- Physical Therapists
- Nutritionists
Patient Advocacy and Education
Understanding your rights and responsibilities as a patient is fundamental to receiving optimal care. Patient advocacy involves being an active participant in your healthcare journey, making informed decisions, and effectively communicating with your healthcare team. The emergence of digital health tools, including AI-powered platforms like X-ray Interpreter, has made medical information more accessible than ever, though it's crucial to verify information through reliable sources.
| Advocacy Area | Key Rights | Patient Actions | Provider Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Information | Access to records | Ask questions | Explain clearly |
| Treatment | Informed consent | Research options | Provide choices |
| Privacy | Data protection | Control sharing | Maintain confidentiality |
| Second Opinion | Alternative views | Seek other doctors | Facilitate referrals |
Research and Clinical Trials
For those interested in contributing to medical knowledge or accessing cutting-edge treatments, participation in clinical trials might be an option. Modern research into exophytic conditions continues to advance our understanding and treatment capabilities.
The Path Forward: Living Well with Exophytic Conditions
Managing an exophytic condition is often a long-term journey that requires patience, dedication, and a proactive approach to health care. The good news is that modern medicine offers numerous tools and approaches for successful management. Many patients find that with proper care and attention, they can maintain a high quality of life while effectively managing their condition.
Daily Management Checklist:
- ✓ Medication compliance
- ✓ Symptom monitoring
- ✓ Activity modifications
- ✓ Stress management
- ✓ Healthy lifestyle choices
Long-term Outlook and Prognosis
The prognosis for exophytic conditions varies significantly based on multiple factors, including:
| Factor | Impact on Prognosis | Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Affects treatment options | Targeted approach |
| Size | Influences intervention timing | Regular monitoring |
| Growth rate | Determines urgency | Frequent assessment |
| Overall health | Affects treatment tolerance | Lifestyle optimization |
| Age | Impacts treatment choices | Personalized planning |
Real Patient Case Studies
Understanding real-world experiences can help patients better relate to their own situations. Here are three anonymized case studies that illustrate different presentations and outcomes of exophytic conditions.
Case Study 1: Early Detection Success
| Patient Profile | Clinical Details |
|---|---|
| Age: 45 | Location: Lung |
| Gender: Female | Size: 2.3cm |
| History: Non-smoker | Type: Exophytic nodule |
Presentation: During a routine chest X-ray for annual employment screening, a small exophytic nodule was discovered in the right lung. The patient was asymptomatic and in otherwise good health.
Management Approach:
- Initial discovery through X-ray
- Confirmation with CT scan
- Monthly monitoring for first 3 months
- Biopsy after slight growth noticed
- Early surgical intervention
Outcome: Early detection and prompt intervention led to complete removal with minimal invasion. Five-year follow-up showed no recurrence, highlighting the importance of routine screening.
Case Study 2: Conservative Management
| Patient Profile | Clinical Details |
|---|---|
| Age: 62 | Location: Kidney |
| Gender: Male | Size: 1.5cm |
| History: Hypertension | Type: Exophytic mass |
Presentation: Incidental finding during ultrasound for hypertension workup. The patient had mild flank discomfort but no other symptoms.
Management Approach:
- Regular imaging surveillance
- Blood pressure management
- Lifestyle modifications
- Active monitoring protocol
Outcome: After two years of monitoring, the growth remained stable with no significant changes. This case demonstrates that not all exophytic growths require immediate surgical intervention.
Case Study 3: Complex Management
| Patient Profile | Clinical Details |
|---|---|
| Age: 33 | Location: Skin |
| Gender: Non-binary | Size: Multiple lesions |
| History: Autoimmune condition | Type: Exophytic growths |
Progression Timeline:
| Time | Event | Action Taken |
|---|---|---|
| Month 0 | Initial presentation | Biopsy and imaging |
| Month 3 | Growth acceleration | Medical therapy initiated |
| Month 6 | Partial response | Combination therapy |
| Month 12 | Stabilization | Maintenance protocol |
Management Challenges:
- Multiple growth sites
- Underlying condition complications
- Treatment resistance
- Quality of life impact
Resolution: Successful management through combination therapy, highlighting the importance of personalized treatment approaches and patience in complex cases.
Key Lessons from Case Studies
-
Early Detection
- Regular screening importance
- Value of routine imaging
- Prompt follow-up on findings
-
Management Options
- Not all cases require surgery
- Individualized approach necessity
- Regular monitoring value
-
Patient Factors
- Age considerations
- Overall health impact
- Lifestyle modifications
| Factor | Impact on Treatment Choice | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Treatment tolerance | Conservative vs. aggressive |
| Location | Accessibility | Surgical vs. monitoring |
| Size | Urgency | Immediate vs. delayed |
| Growth Rate | Risk assessment | Monitoring frequency |
These case studies demonstrate the variety of presentations and management approaches in exophytic conditions. They reinforce the importance of:
- ✓ Individual assessment
- ✓ Regular monitoring
- ✓ Flexible treatment plans
- ✓ Patient engagement
- ✓ Long-term follow-up
Note: These case studies are composites based on typical presentations and do not represent specific individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions About Exophytic Lesions
What is the difference between Exophytic and endophytic lesion?
| Feature | Exophytic | Endophytic |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Direction | Outward from organ surface | Inward into organ |
| Appearance | Protruding mass | Internal growth |
| Detection | Often visible on surface | Requires imaging |
| Common Locations | Skin, organs with surfaces | Deep organ tissue |
An easy way to remember:
- Exophytic = Growing "Exit" (outward)
- Endophytic = Growing "Enter" (inward)
What causes Exophytic lesion?
Several factors can lead to exophytic lesions:
- Cellular growth abnormalities
- Inflammatory responses
- Trauma or injury
- Genetic factors
- Environmental triggers
Common causes include:
- Infections
- Benign tumors
- Malignant growths
- Cystic formations
- Inflammatory conditions
What is an Exophytic myoma?
An exophytic myoma is a specific type of uterine fibroid that:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Grows outward from uterine surface |
| Appearance | Pedunculated (on a stalk) |
| Size | Can vary significantly |
| Effects | May press on nearby organs |
Key points about exophytic myomas:
- Usually benign
- Can grow quite large
- May cause pressure symptoms
- Often discovered during imaging
- May require surgical removal if symptomatic
What is an exophytic cyst?
An exophytic cyst is a fluid-filled sac that grows outward from an organ's surface.
Characteristics include:
- Protrudes from organ surface
- Contains fluid or semi-solid material
- May be single or multiple
- Can vary in size
- Usually well-defined borders
| Type | Common Location | Typical Features |
|---|---|---|
| Simple | Kidney, Liver | Clear fluid-filled |
| Complex | Various organs | Mixed content |
| Hemorrhagic | Any surface | Blood-containing |
| Inflammatory | Various | Associated inflammation |
How do you treat an exophytic lesion?
Treatment approaches vary based on:
- Type of lesion
- Location
- Size
- Symptoms
- Patient factors
Treatment Options Table:
| Treatment | Best For | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Observation | Small, asymptomatic | Regular monitoring needed |
| Medication | Inflammatory lesions | May not remove lesion |
| Minimally invasive surgery | Accessible lesions | Less recovery time |
| Traditional surgery | Large/complex lesions | Longer recovery |
| Ablation | Selected cases | Not suitable for all |
Factors Affecting Treatment Choice:
- Patient age and health
- Lesion characteristics
- Risk of complications
- Available expertise
- Patient preference
Treatment Success Rates
| Approach | Success Rate | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring | N/A | None |
| Medical | 40-60% | Varies |
| Surgery | 80-95% | 2-6 weeks |
| Ablation | 70-85% | 1-2 weeks |
Remember: Treatment decisions should always be individualized and made in consultation with healthcare providers who can assess your specific situation.
Key Points Summary
| Aspect | Important Notes |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis | Imaging usually required |
| Treatment | Multiple options available |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Follow-up | Regular monitoring important |
| Prevention | Not always possible |
For specific medical imaging analysis of exophytic lesions, tools like X-ray Interpreter can provide preliminary insights, though professional medical evaluation is always necessary for definitive diagnosis and treatment planning.
Looking to the Future
Medical science continues to advance, bringing new hope and treatment options for those with exophytic conditions. Staying informed about these developments while maintaining regular medical care provides the best foundation for long-term success. Remember that your healthcare team is there to support you, and new tools and technologies are constantly being developed to improve patient care and outcomes.
Final Thoughts and Additional Resources
- Join patient support groups
- Utilize medical tracking apps
- Connect with advocacy organizations
- Stay informed about new research
- Maintain open communication with your healthcare team
Remember that while this information provides a comprehensive overview, each person's experience with exophytic conditions is unique. Working closely with your healthcare providers to develop and adjust your personal treatment plan remains the cornerstone of successful management.
Note: This information is for educational purposes only. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized medical advice and treatment decisions.