A refined AI tool using facial landmark detection improves the objective evaluation of facial palsy severity in clinical videos.
Key Details
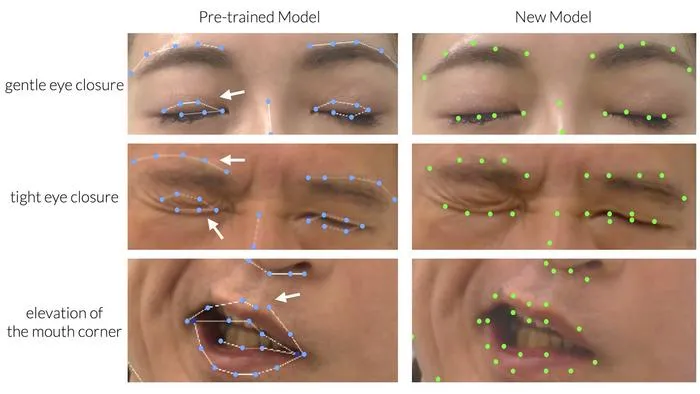
- 1Researchers fine-tuned a facial recognition AI model (3D-FAN) for patients with facial palsy using 1,181 images from 196 patients.
- 2Manual annotation of facial keypoints improved the model's accuracy, particularly for eyelids and mouth asymmetry.
- 3The refined tool showed lower error rates in keypoint detection compared to baseline models trained on healthy faces.
- 4Objective ratings from the model may aid treatment planning and outcome assessments.
- 5Authors plan to make the AI model freely available for wider clinical and research use.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

AI Tool Predicts Risks for Cancer Patients After Heart Attack
A new AI-powered risk prediction model assists clinicians in treating cancer patients following a heart attack by combining oncology and cardiovascular data.

Large Language Models Rival Physicians in Complex Lung Cancer Decisions
A real-world study reveals that large language models (LLMs) can match or exceed human physicians' performance in challenging lung cancer case decision-making, especially for rare cases.

Intelligent Medicine Journal Rises in International Influence Rankings
Intelligent Medicine ranks 66th in China's top internationally influential journals, reflecting its impact in AI-driven clinical research.