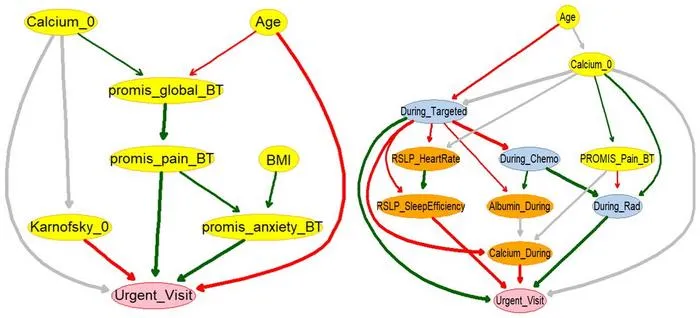
Moffitt Cancer Center researchers created machine learning models that use patient-reported outcomes and wearable data to predict urgent care visits for non-small cell lung cancer patients.
Key Details
- 1Machine learning models incorporated wearable sensor data (Fitbit) and quality-of-life surveys from 58 non–small cell lung cancer patients.
- 2Models using patient-reported and wearable data outperformed those using only clinical/demographic data in predicting urgent care visits during systemic therapy.
- 3Researchers employed explainable Bayesian Networks, revealing how symptom, sleep, and lab data affect risk.
- 4Study highlights potential to proactively intervene and prevent hospitalizations due to treatment complications.
- 5This was a single-center study with a modest sample; larger validation is planned.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

ML and Multimodal Imaging Power Cerebral Blood Flow Monitoring for Spaceflight
Researchers developed a machine learning model that uses ultrasound and MRI data to predict cerebral blood flow in simulated microgravity for astronaut health.

Deep Learning Model Predicts Language Outcomes After Cochlear Implants Using MRI
AI model using deep transfer learning accurately predicts spoken language outcomes in deaf children after cochlear implantation based on pre-implantation brain MRI scans.

LSTM Deep Learning Enhances Optical Sensing for Biochemical and Medical Applications
Researchers have developed an LSTM-driven interferometric sensing system that achieves both high sensitivity and wide measurement range, overcoming previous trade-offs in optical sensing.