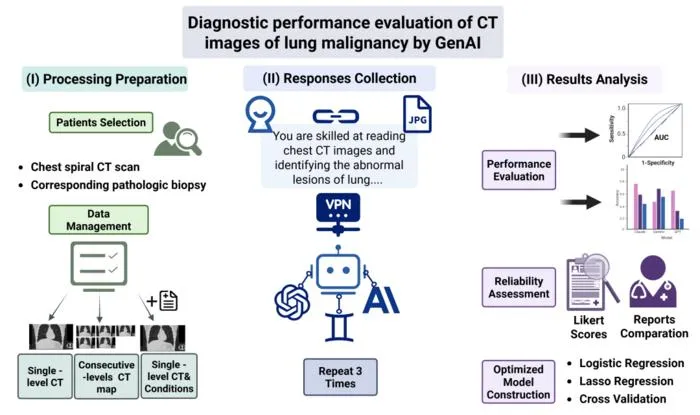
A new study evaluates the diagnostic accuracy of three leading generative multimodal AI models in interpreting CT images for lung cancer detection.
Key Details
- 1Three models compared: Gemini-pro-vision (Google), Claude-3-opus (Anthropic), and GPT-4-turbo (OpenAI).
- 2On 184 malignant lung cases, Gemini achieved highest single-image accuracy (>90%), followed by Claude-3-opus, GPT lowest (65.2%).
- 3Gemini's performance dropped to 58.5% with continuous CT slices, indicating challenges with spatial reasoning in imaging.
- 4Simplified text prompts improved diagnostic AUCs: Gemini (0.76), GPT (0.73), and Claude (0.69).
- 5Claude-3-opus showed superior consistency and lower variation in lesion feature analysis.
- 6External validation with TCGA and MIDRC datasets supported findings, especially with simplified prompt strategies.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

AI and Advanced Microscopy Unveil Cell's Exocytosis Nanomachine
Researchers have discovered the ExHOS nanomachine responsible for constitutive exocytosis using advanced microscopy and AI-enhanced image analysis.

Physical Activity Linked to Breast Tissue Biomarkers in Teens
A study links adolescent recreational physical activity to changes in breast tissue composition and stress biomarkers, potentially impacting future breast cancer risk.

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.