GenAI models demonstrate high accuracy and consistency in pathological grading and risk assessment for lung adenocarcinoma.
Key Details
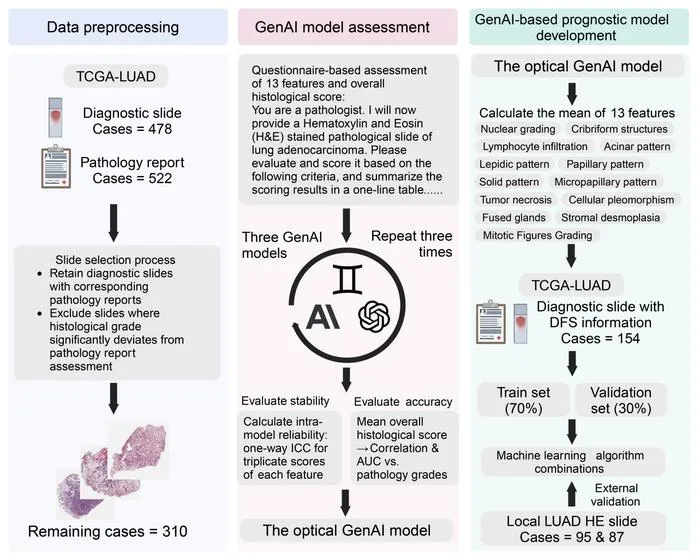
- 1Study tested GPT-4o, Claude-3.5-Sonnet, and Gemini-1.5-Pro on 492 digitized slides from public and independent sources.
- 2Claude-3.5-Sonnet achieved 82.3% accuracy in lung adenocarcinoma grading, with strong repeatability.
- 3Models extracted 11 histological features and 4 clinical variables for comprehensive risk assessment.
- 4Diagnostic and prognostic tasks were completed in minutes, much faster than human experts.
- 5AI models reduced inter-observer variability and enabled objective, standardized analysis across multiple samples.
- 6GenAI models surfaced new significant prognostic factors including interstitial fibrosis and papillary patterns.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

AI and Advanced Microscopy Unveil Cell's Exocytosis Nanomachine
Researchers have discovered the ExHOS nanomachine responsible for constitutive exocytosis using advanced microscopy and AI-enhanced image analysis.

Physical Activity Linked to Breast Tissue Biomarkers in Teens
A study links adolescent recreational physical activity to changes in breast tissue composition and stress biomarkers, potentially impacting future breast cancer risk.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.