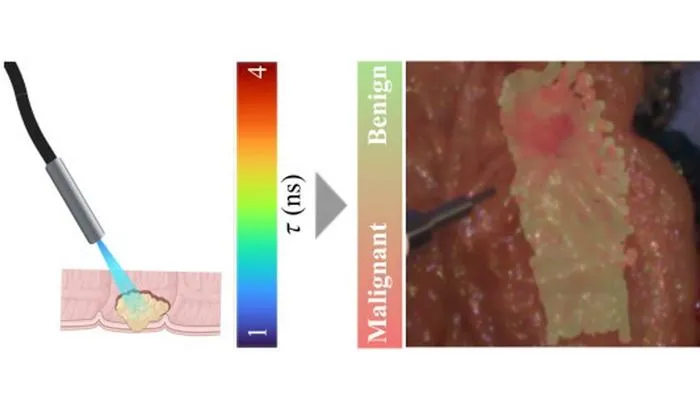
A label-free optical imaging technique using autofluorescence lifetime and AI can distinguish colorectal cancer with 85% accuracy.
Key Details
- 1Champalimaud Foundation researchers developed a fiber-optic, label-free optical imaging method for colorectal tissue analysis.
- 2Technique involves autofluorescence lifetime measurements at two wavelengths to capture biochemical differences.
- 3Machine learning (AdaBoost) trained on 117 patients' surgical specimens, validated with matched pathology results.
- 4On test data, the AI achieved 85% accuracy, 85% sensitivity, and 85% specificity.
- 5Potential applications include real-time cancer detection during colonoscopy or surgery, reducing the need for biopsies.
- 6Simplified versions of the imaging system delivered strong results, supporting future clinical use.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

AI and Advanced Microscopy Unveil Cell's Exocytosis Nanomachine
Researchers have discovered the ExHOS nanomachine responsible for constitutive exocytosis using advanced microscopy and AI-enhanced image analysis.

Physical Activity Linked to Breast Tissue Biomarkers in Teens
A study links adolescent recreational physical activity to changes in breast tissue composition and stress biomarkers, potentially impacting future breast cancer risk.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.