RadAI Slice Newsletter Weekly Updates in Radiology AI |
Good morning, there. A generative AI model predicted timing and risk for over 1,000 diseases from 400,000 UK Biobank records. Large-scale AI health record modeling enables new approaches for preventive and population health strategies. While not clinic-ready, robust external validation moves the field closer to actionable risk stratification and scenario simulation. Radiologists will increasingly intersect with these tools for precision diagnostics, population health, and integrated imaging analytics. PS: If this touches your work, hit Reply with one note. I read every message.
Here's what you need to know about Radiology AI last week: AI predicts long-term disease risk from large health record datasets Joint Commission and CHAI release detailed AI governance guidance AI halves false positives in multicenter lung cancer CT screening AI-driven analysis of routine mammograms predicts cardiovascular risk Plus: 4 FDA approved devices & 4 new papers.
|
📈 AI predicts long-term disease risk from large health record datasets  Image from: EurekAlert RadAI Slice: A new generative AI model uses health records to forecast disease risk and timing at scale. The details: Trained on 400,000 UK Biobank participants, validated on 1.9M Danish records Excels at predicting chronic, progressive diseases like heart attacks and cancers Forecasts are probabilistic, favor population risk, best for short-term predictions Model less effective for childhood/adolescent events and some minoritized groups Not yet for clinical use—intended for research, scenario-simulation, and disease modeling
Key takeaway: Validated, large-scale transformer models may evolve disease prediction and health system planning. Radiology may see new intersection as AI guides imaging protocols and risk-based screening at the population level. |
🏛️ Joint Commission and CHAI release detailed AI governance guidance  Image from: AI in Healthcare RadAI Slice: Healthcare institutions now have initial industry-wide guidance for safe, consistent use of AI in clinical imaging and diagnostics. The details: Framework covers governance, risk reporting, model monitoring, end-user training Playbooks and voluntary certification coming for 22,000+ accredited facilities Radiology cited in guidance and highlighted advances (e.g., lung CT AI) Feedback invited for updates; emphasis is on evolving with the field Parallels ongoing European and US policy developments in imaging AI
Key takeaway: New guidance offers radiology departments a blueprint for robust clinical AI oversight, supporting safer implementation and external accountability as deployments scale nationally. |
🔍 AI halves false positives in multicenter lung cancer CT screening 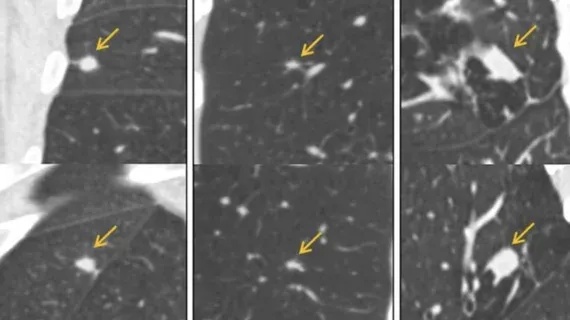 Image from: Health Imaging RadAI Slice: International validation shows AI can substantially reduce false-positive rates in lung CT screening. The details: AI trained on 16k nodules from NLST, validated on >4,000 patients and ~8,000 nodules False positives for lung cancer reduced by nearly 50% compared to standard methods Prospective, multi-site trial strengthens evidence for clinical deployment Reduces unnecessary procedures, cost, and patient anxiety Robust external validation essential for adoption in population screening
Key takeaway: Robustly validated AI can make national lung screening programs more efficient and patient-centered. Lowering false positives addresses major barriers to broader CT screening acceptance. |
🩺 AI-driven analysis of routine mammograms predicts cardiovascular risk RadAI Slice: Large cohort study shows mammograms, combined with AI, predict women's cardiovascular risk as accurately as traditional clinical risk calculators. The details: Model trained and validated on 49,196 women with median 8.8-year follow-up AI achieved c-index 0.72; adding clinical data raised c-index to 0.75 3,392 women had major cardiovascular events, enabling robust modeling Designed for opportunistic risk assessment at breast cancer screening Potential to augment preventive care with no added patient burden
Key takeaway: Leveraging routine mammograms with AI may offer a dual-screening pathway—supporting both cancer detection and proactive cardiovascular risk management for women in a single imaging study. |
🏛️ FDA Clearances K252608 - AI-Rad Companion Prostate MR (Siemens)—FDA-cleared for prostate MRI reading assistance with AI-based detection of prostate cancer features. K251682 - MuscleView 2.0 (Springbok)—510(k) cleared system for MRI-based muscle tissue visualization and analysis in musculoskeletal radiology. K251399 - SIGNA™ Sprint (GE)—New high-performance MRI system cleared for broad clinical diagnostic use. K252477 - Hybrid Viewer (Hermes Medical Solutions)—510(k) cleared for PET tomographic image review and analysis in clinical practice. Explore last week's 11 radiology AI FDA approvals.
|
📄 Fresh Papers doi:10.1016/j.chest.2025.08.034 - A prospective multicenter machine learning model integrating radiomics and clinical data predicts usual interstitial pneumonia with AUC up to 0.80, matching expert performance. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjaf031 - A multimodal CNN-Transformer fused MRI and clinical data for HCC immunotherapy response, outperforming single-modal models (AUC 0.785 on validation). doi:10.3174/ajnr.A9016 - Multi-center outcome modeling using perfusion CT and deep learning outperformed threshold-based methods (Dice up to 50%) for stroke lesion prediction. doi:10.1148/ryai.240861 - Large-scale analysis of 28,278 mammograms shows acquisition variables impact both AI and human breast cancer detection—often in different ways. Browse 192 new radiology AI studies from last week.
|
That's it for today! Before you go we’d love to know what you thought of today's newsletter to help us improve the RadAI Slice experience for you. |
|
👋 Quick favor: drag this into your Primary tab so you don’t miss next week. Or just hit Reply with one thought. See you next week. |
|