International study highlights demographic biases in AI models diagnosing skin diseases from images.
Key Details
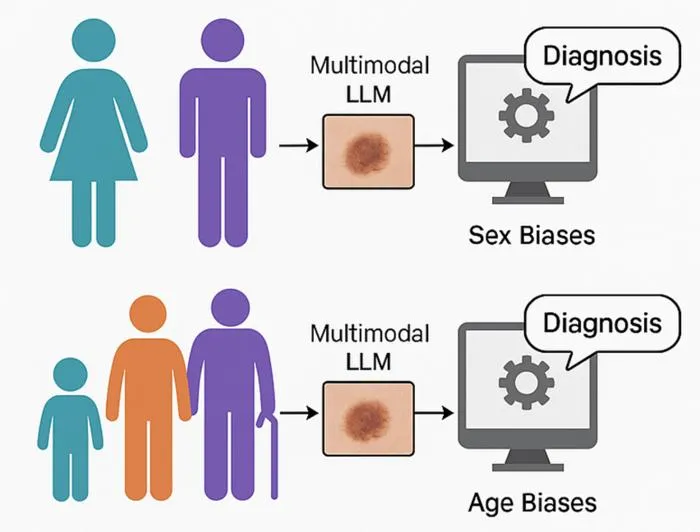
- 1Researchers evaluated ChatGPT-4 and LLaVA on 10,000 dermatoscopic images of skin diseases.
- 2Study assessed diagnostic accuracy and fairness regarding sex and age groups.
- 3ChatGPT-4 showed better demographic fairness than LLaVA, which had marked sex-based biases.
- 4Both AI models outperformed traditional deep learning approaches overall.
- 5Calls made for considering demographic fairness before clinical deployment of AI in healthcare.
- 6Further research planned to evaluate impact of skin tone and other demographic factors.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Dual-Branch Graph Attention Network Predicts ECT Success in Teen Depression
Researchers developed a dual-branch graph attention network that uses structural and functional MRI data to accurately predict individual responses to electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with major depressive disorder.