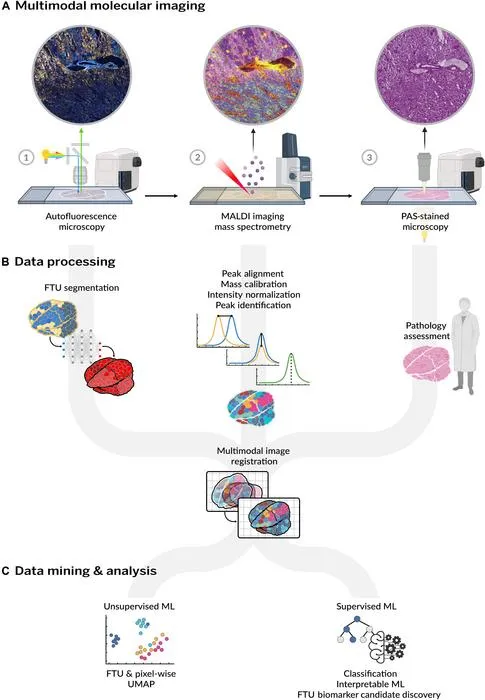
Vanderbilt researchers created the first high-resolution kidney lipid atlas using advanced imaging and machine learning, mapping over 100,000 tissue units.
Key Details
- 1Study published in Science Advances in June 2025 by Vanderbilt and Delft University teams.
- 2Mapped lipid profiles across more than 100,000 functional units in 29 donor kidneys using MALDI imaging mass spectrometry and microscopy.
- 3Applied multimodal registration and interpretable machine learning to co-register and analyze datasets.
- 4Identified molecular signatures tied to specific kidney structures and disease risk factors such as BMI and sex.
- 5Data and analysis tools are publicly available through NIH's HuBMAP program.
- 6Project funded by multiple NIH institutes and the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Dual-Branch Graph Attention Network Predicts ECT Success in Teen Depression
Researchers developed a dual-branch graph attention network that uses structural and functional MRI data to accurately predict individual responses to electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with major depressive disorder.