Deep Learning Model Enables 3D Handheld Photoacoustic-Ultrasound Imaging Without Sensors
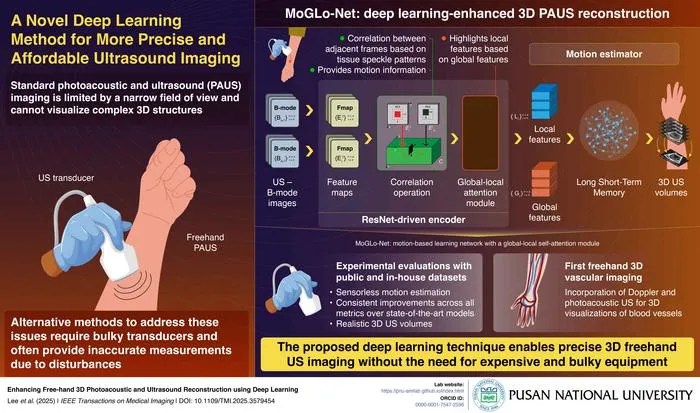
Pusan National University develops MoGLo-Net, an AI model that reconstructs 3D images from handheld 2D photoacoustic and ultrasound scans without external sensors.
Key Details
- 1MoGLo-Net uses deep learning to track handheld ultrasound transducer motion from tissue speckle data, eliminating need for external tracking hardware.
- 2Combines ResNet-based encoder and LSTM-based motion estimator for accurate motion tracking and 3D reconstruction.
- 3Validated using both proprietary and public datasets, outperforming state-of-the-art methods on all metrics.
- 4Successfully achieved 3D blood vessel reconstructions from combined ultrasound and photoacoustic data.
- 5Published June 13, 2025, in IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging (DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2025.3579454).
- 6Innovation aims to make advanced 3D imaging safer, more accurate, and accessible without costly hardware.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Dual-Branch Graph Attention Network Predicts ECT Success in Teen Depression
Researchers developed a dual-branch graph attention network that uses structural and functional MRI data to accurately predict individual responses to electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with major depressive disorder.