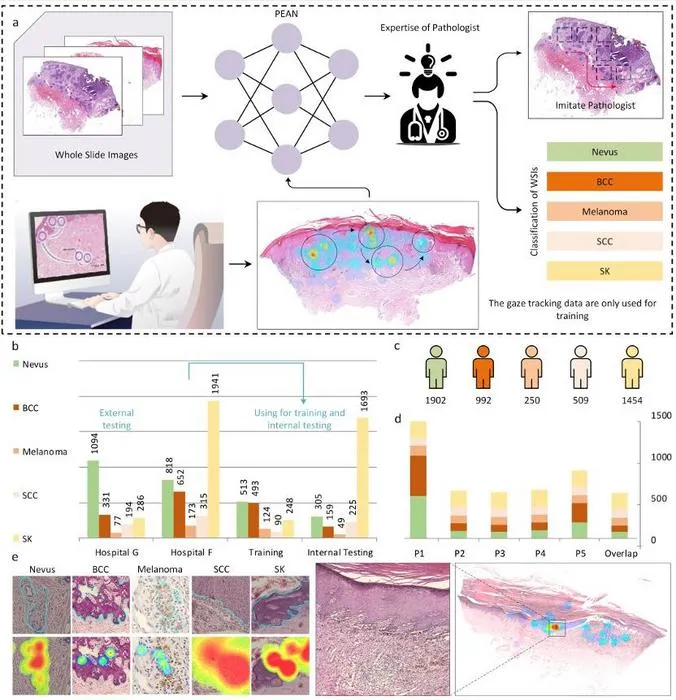
Researchers developed a deep learning system using eye-tracking data to enhance AI-powered biopsy image interpretation.
Key Details
- 1The Pathology Expertise Acquisition Network (PEAN) was trained using expert pathologists’ eye movements while reviewing 5,881 skin lesion slides.
- 2PEAN-C achieved 96.3% accuracy and 0.992 AUC on internal data and 93.0% accuracy and 0.984 AUC on external test data, exceeding the next best AI model by 5.5%.
- 3Using pathologist gaze data, the model identifies relevant tissue regions with much less manual labeling burden than traditional pixel-wise annotation.
- 4Integrating PEAN-generated data with other models improved classification accuracy and AUC, statistically significant by paired t-test (p = 0.0053 and 0.0161).
- 5The aim is to scale to personalized diagnosis and multimodal predictive models, leveraging low-cost data collection from expertise monitoring.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Deep Learning Boosts ICD-11 Coding Accuracy for Chinese EMRs
Researchers developed a deep learning model achieving high accuracy in automatic ICD-11 coding of Chinese electronic medical records.