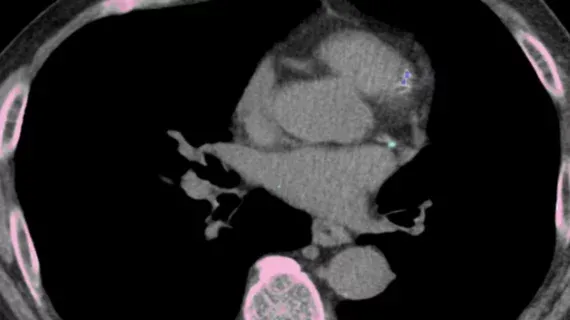
AI may enable more accurate tracking of coronary artery calcium (CAC) growth using routine lung cancer screening CT scans.
Key Details
- 1CAC is commonly found incidentally in up to 12% of lung cancer screening patients.
- 2Increases in CAC scores between screenings are strongly correlated with heightened risk of adverse cardiovascular events.
- 3Debate exists on the clinical significance of CAC growth over time due to insufficient study.
- 4AI is proposed as a tool to overcome technical challenges, such as lack of ECG gating, in longitudinal CAC assessment on low-dose CT scans.
- 5Annual lung cancer CT screenings present opportunities for repeated CAC monitoring.
Why It Matters
This development could allow radiologists to leverage existing lung cancer screening CTs for dual cardiovascular risk monitoring, potentially leading to earlier detection of patients at risk for adverse events. Integrating AI for automated CAC tracking may improve clinical efficiency and patient outcomes.

Source
Health Imaging
Related News

•AuntMinnie
Deep Learning AI Outperforms Radiologists in Detecting ENE on CT
A deep learning tool, DeepENE, exceeded radiologist performance in identifying lymph node extranodal extension in head and neck cancers using preoperative CT scans.

•Radiology Business
Patients Favor AI in Imaging Diagnostics, Hesitate on Triage Use
Survey finds most patients support AI in diagnostic imaging but are reluctant about its use in triage decisions.

•Radiology Business
FDA Clears Multi-Disease AI Screening Platform for CT Imaging
HeartLung Corporation's AI-CVD platform receives FDA clearance to detect multiple diseases from a single CT scan.