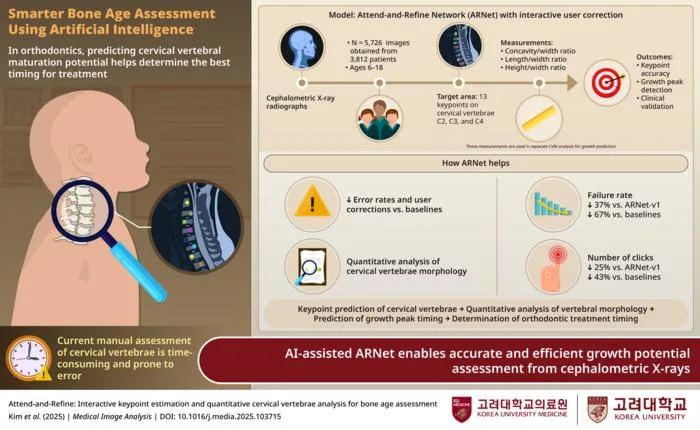
Korean researchers developed an AI system (ARNet-v2) that predicts children's growth spurts from neck X-rays to enhance orthodontic treatment planning.
Key Details
- 1ARNet-v2 uses lateral cephalometric radiographs to identify cervical vertebrae keypoints.
- 2The model allows a single clinician correction to propagate, boosting efficiency and accuracy.
- 3Tested on 5,700+ radiographs and across four public datasets, ARNet-v2 reduced prediction failures by up to 67%.
- 4Manual annotation requirements are halved compared to conventional approaches.
- 5The AI may reduce the need for additional hand–wrist X-rays, lowering radiation exposure for pediatric patients.
- 6Published in Medical Image Analysis, July 2025.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

EU SHASAI Project Aims to Fortify AI Security Across Sectors
The SHASAI project will enhance AI system security through lifecycle-spanning methods tested in real-world scenarios, including healthcare.

Generative AI Significantly Improves Denoising of fMRI Brain Data
Boston College researchers developed a generative AI method that removes noise from fMRI brain scans, achieving over 200% improvement compared to prior techniques.

Deep Learning Model Predicts Language Outcomes After Cochlear Implants Using MRI
AI model using deep transfer learning accurately predicts spoken language outcomes in deaf children after cochlear implantation based on pre-implantation brain MRI scans.