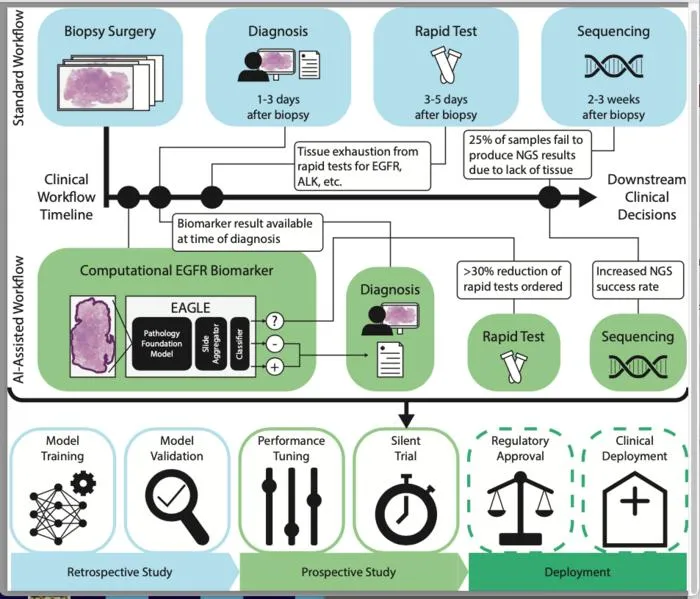
An AI model can accurately flag EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma using routine pathology slides, reducing the need for rapid genetic tests.
Key Details
- 1Researchers from Mount Sinai, Memorial Sloan Kettering, and collaborators published results in Nature Medicine on July 9, 2025.
- 2The AI model predicts EGFR mutations from H&E-stained pathology slides of lung adenocarcinoma.
- 3A live 'silent trial' at Memorial Sloan Kettering showed the model could reduce rapid genetic testing by over 40%.
- 4The model was trained and validated on the largest multi-institutional dataset of matched slides and sequencing results from the US and Europe.
- 5Preserving tissue by avoiding unnecessary rapid tests allows for more comprehensive genomic sequencing.
- 6Work is ongoing to broaden the model's biomarker detection and deploy it in more healthcare settings.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Dual-Branch Graph Attention Network Predicts ECT Success in Teen Depression
Researchers developed a dual-branch graph attention network that uses structural and functional MRI data to accurately predict individual responses to electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with major depressive disorder.