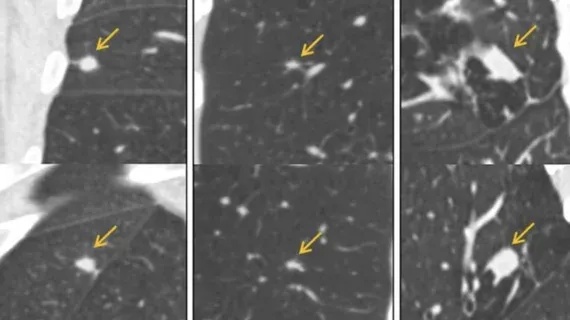
An AI algorithm significantly reduced false positives in lung cancer detection on CT scans, according to international multi-site research.
Key Details
- 1Study published in 'Radiology' evaluated an AI model for lung nodule assessment.
- 2AI was trained on over 16,000 nodules from the National Lung Screening Trial.
- 3Validation used CT datasets from three additional European screening trials.
- 4The algorithm was tested on data from more than 4,000 participants and nearly 8,000 nodules.
- 5Results showed the AI nearly halved the rate of false positives in lung cancer detection.
Why It Matters

Source
Health Imaging
Related News

New Report Highlights Clinical AI Performance, Sustainability, and Adoption Challenges
A multi-institutional review details key challenges, progress, and sustainability concerns in deploying clinical AI in real-world healthcare settings.

FDA Clears AI Platform for Comprehensive Cardiac Risk Assessment on CT
HeartLung Corporation's AI-CVD receives FDA clearance for opportunistic multi-condition screening on routine chest CT scans.

LLM Boosts Terminology Expansion in Radiology Reports Over RadLex
A large language model (LLM) significantly outperforms RadLex in expanding terms for radiology report language standardization.