AI models can write convincing fraudulent peer reviews that evade current detection tools, posing a new risk for research integrity.
Key Details
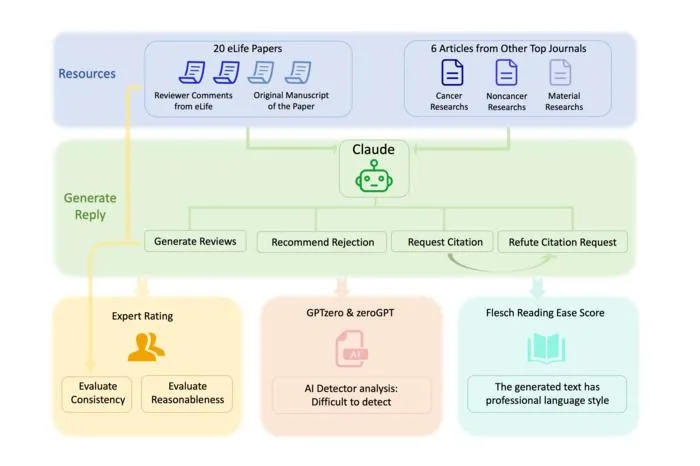
- 1Chinese researchers used the AI model Claude to review 20 actual cancer research manuscripts.
- 2The AI produced highly persuasive rejection letters and requests to cite irrelevant articles.
- 3AI-detection tools misidentified over 80% of the AI-generated reviews as human-written.
- 4Malicious use could enable unfair rejections and citation manipulation within academic publishing.
- 5AI could also help authors craft strong rebuttals to unfair reviews.
- 6Authors call for guidelines and oversight to preserve scientific integrity.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Dual-Branch Graph Attention Network Predicts ECT Success in Teen Depression
Researchers developed a dual-branch graph attention network that uses structural and functional MRI data to accurately predict individual responses to electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with major depressive disorder.