Combining CT-based radiomics and deep learning features with clinical data enhances prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma risk in cirrhosis patients.
Key Details
- 1Study used a multicenter, prospective cohort of 2,411 cirrhosis patients in China (2018–2023).
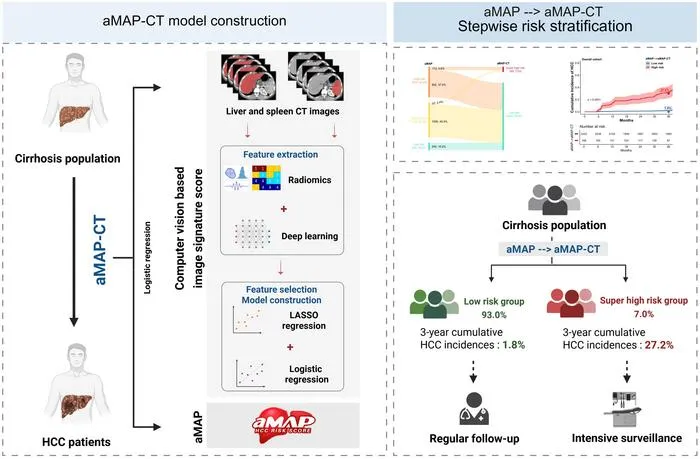
- 2All patients underwent 3-phase contrast-enhanced abdominal CT at baseline.
- 3AI model extracted radiomics (PyRadiomics) and deep learning (ResNet-18) features from liver and spleen on CT.
- 4The integrated aMAP-CT model significantly outperformed standard clinical models (AUC 0.809–0.869).
- 5Model stratified patients into high- (26.3% incidence) and low-risk (1.7%) groups over three years.
- 6Stepwise application identified 7% of patients at very high risk for HCC (27.2% three-year incidence).
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Dual-Branch Graph Attention Network Predicts ECT Success in Teen Depression
Researchers developed a dual-branch graph attention network that uses structural and functional MRI data to accurately predict individual responses to electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with major depressive disorder.