Researchers have developed an AI-enhanced three-phase CT perfusion protocol that reduces radiation exposure by over 80% while accurately generating perfusion maps for stroke evaluation.
Key Details
- 1Traditional CT perfusion (CTP) uses continuous scanning, resulting in high radiation doses (~5260 mGy·cm) and workflow complexity.
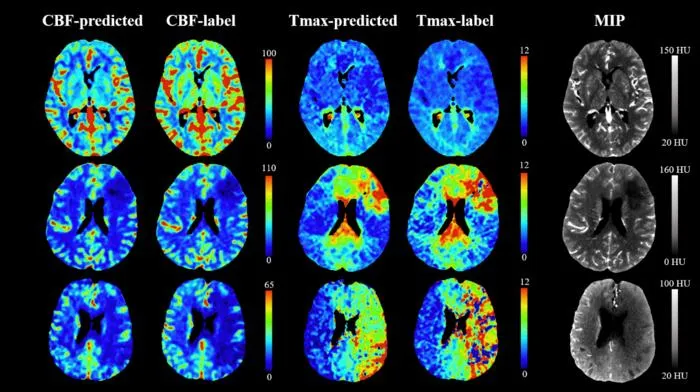
- 2The new protocol samples only three phases and uses a GAN-based deep learning model to generate cerebral blood flow (CBF) and Tmax maps.
- 3The approach reduces patient radiation exposure by more than 80% compared to standard CTP methods.
- 4Internal validation demonstrated high fidelity of AI-generated blood flow maps, even with slight deviations in timing of image acquisition.
- 5The method preserves diagnostic accuracy essential for stroke management and is more robust to patient motion.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Dual-Branch Graph Attention Network Predicts ECT Success in Teen Depression
Researchers developed a dual-branch graph attention network that uses structural and functional MRI data to accurately predict individual responses to electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with major depressive disorder.