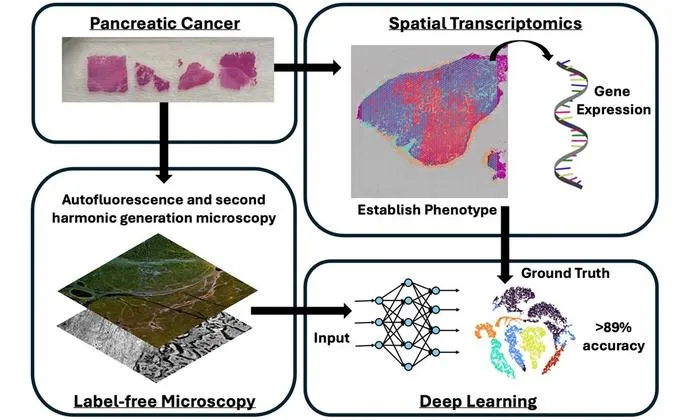
University of Arizona researchers achieved nearly 90% accuracy in pancreatic cancer phenotyping using label-free optical microscopy with deep learning AI.
Key Details
- 1Label-free optical microscopy paired with deep neural networks identified tissue phenotypes at over 89% accuracy in pancreatic cancer samples.
- 2Spatial transcriptomics served as the 'ground truth' for phenotypic classification.
- 3Traditional image analysis could not match the performance of AI methods, pointing to AI's necessity in extracting meaningful features from label-free images.
- 4This approach bypasses expensive and time-intensive molecular/genetic sequencing currently used in precision medicine.
- 5The work demonstrates a significant step toward more accessible and rapid phenotyping for cancer care.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Dual-Branch Graph Attention Network Predicts ECT Success in Teen Depression
Researchers developed a dual-branch graph attention network that uses structural and functional MRI data to accurately predict individual responses to electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with major depressive disorder.