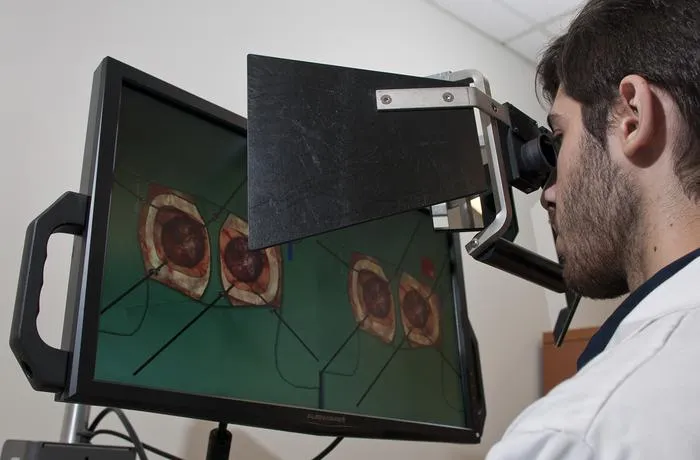
AI-augmented human instruction leads to superior neurosurgical simulator training versus AI or human feedback alone.
Key Details
- 1Study involved 87 medical students from four Quebec medical schools, divided into three training groups.
- 2Groups received (1) AI-only feedback, (2) expert instructor feedback, or (3) expert feedback informed by AI performance data.
- 3Students with AI-informed human feedback showed best surgical skill improvement and risk management.
- 4Findings published in JAMA Surgery (Aug 6, 2025).
- 5Integration of AI analytics with human expertise enhances surgical training and skill transfer.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Dual-Branch Graph Attention Network Predicts ECT Success in Teen Depression
Researchers developed a dual-branch graph attention network that uses structural and functional MRI data to accurately predict individual responses to electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with major depressive disorder.