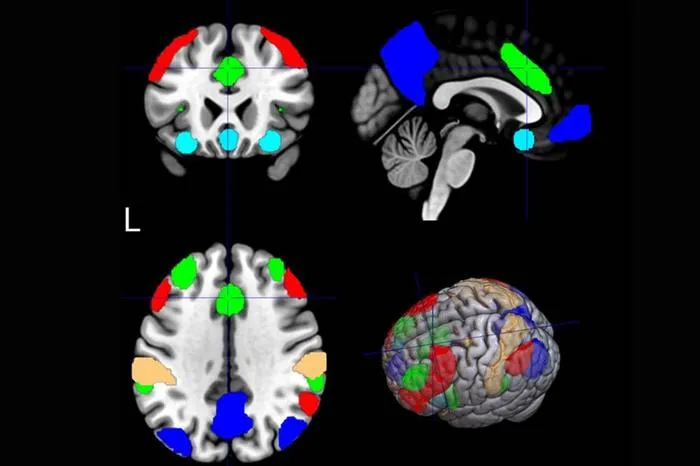
MUSC researchers used machine learning on fMRI scans to predict which smokers would benefit from repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for quitting smoking.
Key Details
- 1MUSC study combines machine learning and fMRI to personalize rTMS for smoking cessation.
- 242 participants took part in an earlier study, split into real vs sham TMS groups.
- 3The salience network's connectivity in the brain, analyzed by AI, correlated best with positive rTMS outcomes.
- 4Machine learning enabled predictions of individual responsiveness to rTMS based on brain network analysis.
- 5Study published in Brain Connectivity; NIH grant support cited.
- 6The research establishes groundwork for precision neuromodulation and larger future trials.
Why It Matters

Source
EurekAlert
Related News

Deep Learning AI Outperforms Clinic Prognostics for Colorectal Cancer Recurrence
A new deep learning model using histopathology images identifies recurrence risk in stage II colorectal cancer more effectively than standard clinical predictors.

AI Reveals Key Health System Levers for Cancer Outcomes Globally
AI-based analysis identifies the most impactful policy and resource factors for improving cancer survival across 185 countries.

Dual-Branch Graph Attention Network Predicts ECT Success in Teen Depression
Researchers developed a dual-branch graph attention network that uses structural and functional MRI data to accurately predict individual responses to electroconvulsive therapy in adolescents with major depressive disorder.